
SỬ DỤNG KHÁNG SINH TRONG NHIỄM KHUẨN GRAM ÂM ĐA KHÁNG
PGS. TS. BS PHÙNG NGUYỄN THẾ NGUYÊN


Trưởng Bộ Môn Nhi – ĐHYD TPHCM Trưởng Khoa Hồi Sức Nhiễm – BVNĐ1

Nội dung
- Tình hình kháng kháng sinh của vi khuẩn gram âm
- Cơ chế kháng của vi khuẩn gram âm
- Hướng dẫn điều trị hiện nay
- Kết luận

1. Vi khuẩn đa kháng
WHO priority bacterial pathogens list for research and development of new antibiotics.a
cterial Pathogen
inetobacter baumannii, carbapenem-resistant eudomonas aeruginosa, carbapenem-resistant terobacteriaceae,b carbapenem-resistant, 3rd generation phalosporin-resistant
ycobacteria, including Mycobacterium tuberculosis
terococcus faecium, vancomycin-resistant aphylococcus aureus, methicillin-resistant, vancomycin termediate and resistant
licobacter pylori, clarithromycin-resistant mpylobacter, fluoroquinolone-resistant lmonella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant
isseria gonorrhoeae, 3rd generation cephalosporin-resistant, oroquinolone-resistant
eptococcus pneumoniae, penicillin-non-susceptible
ESKAPE pathogens:
Thời gian ở BV dài, tỷ lệ tử vong cao Thuốc mắc, hiệu quả có thể kém, tác dụng phụ nhiều |
|
| Priority Ba | |
| Critical Ac Ps En ce M
High En St in He Ca Sa Ne flu Medium Str |
Haemophilus influenza, ampicillin-resistant
Shigella spp., fluoroquinolone-resistant C. González-Bello / Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 27 (2017) 4221–4228
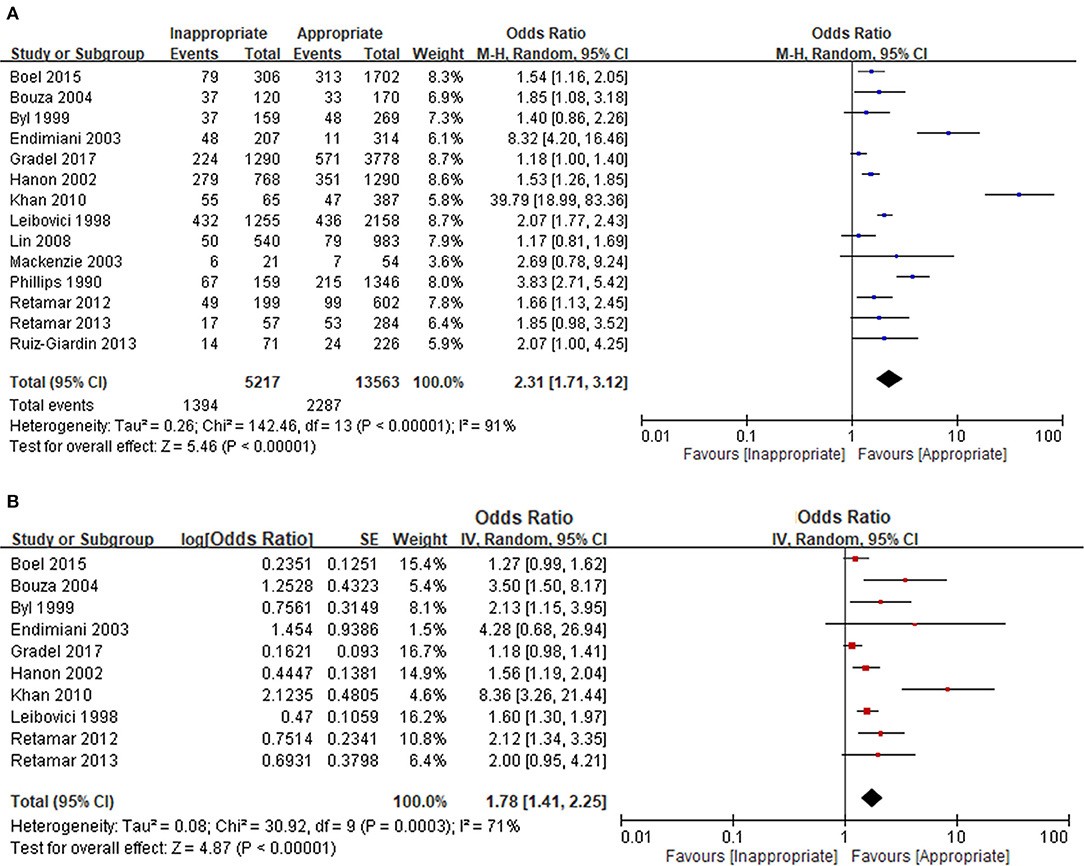 Dùng KS không thích hợp và tử vong
Dùng KS không thích hợp và tử vong
Dùng KS không thích hợp trong NKH tăng tỷ lệ tử vong 1.46; Với VK đa kháng tăng 9.09
Adjusted odds ratio
 Infectious Diseases – Surveillance, Prevention and Treatment Volume 9 – 2022
Infectious Diseases – Surveillance, Prevention and Treatment Volume 9 – 2022
Adjusted odds ratio
Sameer S Kadri et all , Lancet Infect Dis 2020
A
3
2
1
0
All
Staphylococcus β-haemolytic
aureus streptococcus
Enterococcus Enterobacteriaceae Non-glucose spp spp fermenters
B
3
2
1
0
Bloodstream infections
Sepsis without shock
Septic shock
Antibiotic- resistant phenotype
Antibiotic- susceptible phenotype

Tính kháng của đơn vị, quyết định chọn KS




 Nhiễm khuẩn gram âm và kháng thuốc
Nhiễm khuẩn gram âm và kháng thuốc
84,2% NKBV do vi khuẩn gram âm
- A. baumanii 24,4%, P. aeruginosa 13,8% và K. Pneumonia 11.6%
- Tỷ lệ kháng carbapenem: A. baumanii 89,2%, P. aeruginosa 55,7% và K. Pneumonia 14,9%
Phu VD, et al. (2016) Burden of Hospital Acquired Infections and Antimicrobial Use in Vietnamese Adult Intensive Care Units. PLoS ONE 11(1): e0147544.
Hồ Chí Minh: BVNĐ1 2016-2021
VI KHUẨN GRAM ÂM
800
700
726
631
600
500
524
453
462
400
300
305
380
423
398
329
302
250
230
200
176
138
202
199
115
100
0
26 35
44 37
43 60 38
72 50 66
7 7
 2016
2016
Acin2e0to1b7acter spp Escherichia coli
2018Haemophilus influenzae Kleb2s0ie1l9la pneumoniae Pseudomona2s02ae0ruginosa
2021
Dữ liệu vi sinh do BCV cung cấp

Antibiotic name
K
| háng kháng sinh
Tại BVNĐ1 2020 |
Acinetobacter
spp (N=217), % |
Escherichia coli
(N=295), % |
Klebsiella spp (N=258), % | Pseudomonas aeruginosa
(N=106), % |
Enterobacter spp (N=39), % | |
| Ampicillin | – | 97,3 | – | – | 97,4 | |
| Cefotaxime | 83,8 | 73,5 | 69,4 | – | 56,4 | |
| Ceftriaxone | 86,2 | 80,7 | 76,7 | – | 61,5 | |
| Ceftazidime | 82,9 | 54,5 | 61,6 | 21,7 | 56,4 | |
| Cefuroxime | 86,4 | 79,8 | 78,4 | – | 59 | |
| Cefepime | 80,1 | 38,3 | 52,3 | 19,8 | 38,9 | |
| Chloramphenicol | – | 26,5 | 24 | – | 30,7 | |
| Ciprofloxacin | 73,7 | 70,2 | 47,3 | 18,9 | 53,8 | |
| Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole | 34,5 | 72,9 | 54,3 | – | 61,5 | |
| Gentamicin | 65 | 46,8 | 58,9 | 12,3 | 38,4 | |
| Imipenem | 76,5 | 14,2 | 44,2 | 27.6 | 25,6 | |
| Meropenem | 76,5 | 13,9 | 44,7 | 24,3 | 28,2 | |
| Ertapenem | – | 16,3 | 48,2 | – | 33,3 | |
| Ticarcillin/Clavulanic acid | 77,4 | 30 | 60,1 | 29,7 | 44,7 | |
Dữ liệu vi sinh do BCV cung cấp

 Sử dụng kháng sinh không hợp lý
Sử dụng kháng sinh không hợp lý
CDC 2016: 3 đơn có 1 đơn KS không cần thiết.
- Tỷ lệ còn cao trong chăn nuôi,…

Tác hại của dùng kháng sinh không hợp lý
“Collateral damage” đề cập đến ảnh hưởng của điều trị kháng sinh:
- Tạo các dòng kháng thuốc
Phát triển các vi khuẩn tạm trú (colonization)
- Phát triển các vi khuẩn đa kháng
- Cephalosporin có thể tạo vancomycin-resistant enterococci,
- Klebsiella pneumoniae tiết ESBL, beta-lactam-resistant Acinetobacter sp, Clostridium difficile.
- Quinolone tăng các dòng MRSA và gram âm kháng quinolone
Paterson DL. “Collateral damage” from cephalosporin or quinolone antibiotic
therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004 May 15;38 Suppl 4:S341-5. doi: 10.1086/382690. PMID: 15127367.
Tăng sử dụng kháng sinh carbapenem

Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership – Vietnam, 2008
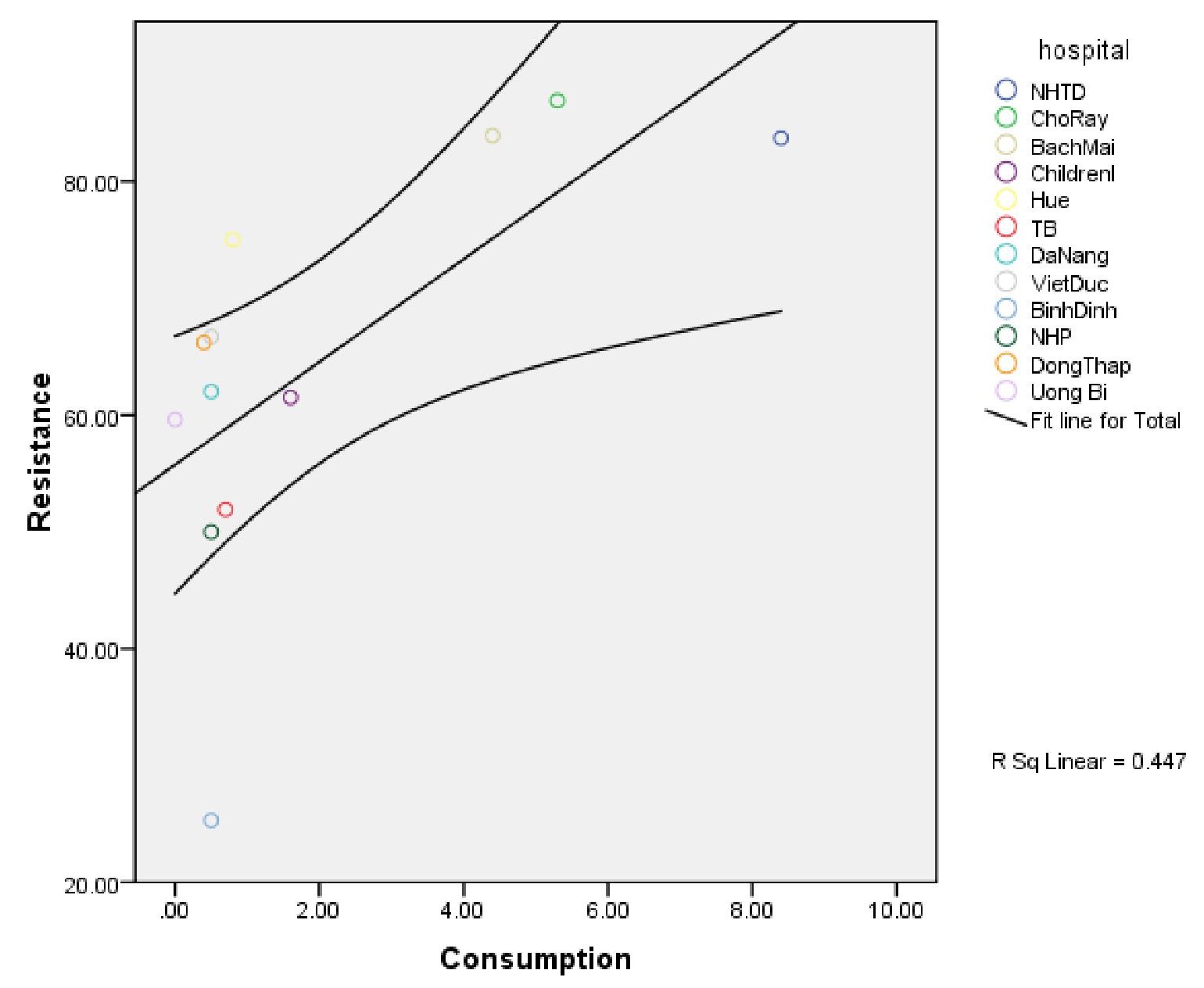
Tăng sử dụng carbapenem, gia tăng kháng Ceftazidim của acinebacter
Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership – Vietnam, 2008
-
-
- 310 bệnh nhân
-
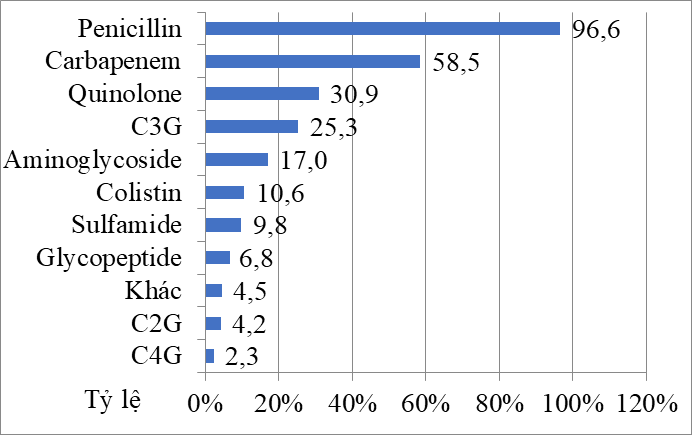
Hình 4. Tỷ lệ kê đơn các nhóm kháng sinh
Đinh Thị Thúy Hà, TẠP CHÍ Y HỌC VIỆT NAM TẬP 501 – THÁNG 4 – SỐ 1 –
2021

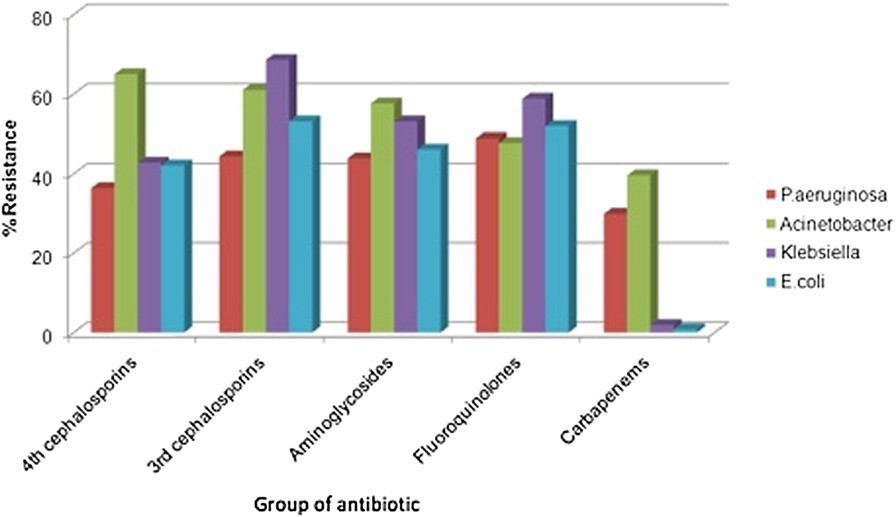 Tăng sử dụng kháng sinh và tỷ lệ kháng thuốc
Tăng sử dụng kháng sinh và tỷ lệ kháng thuốc
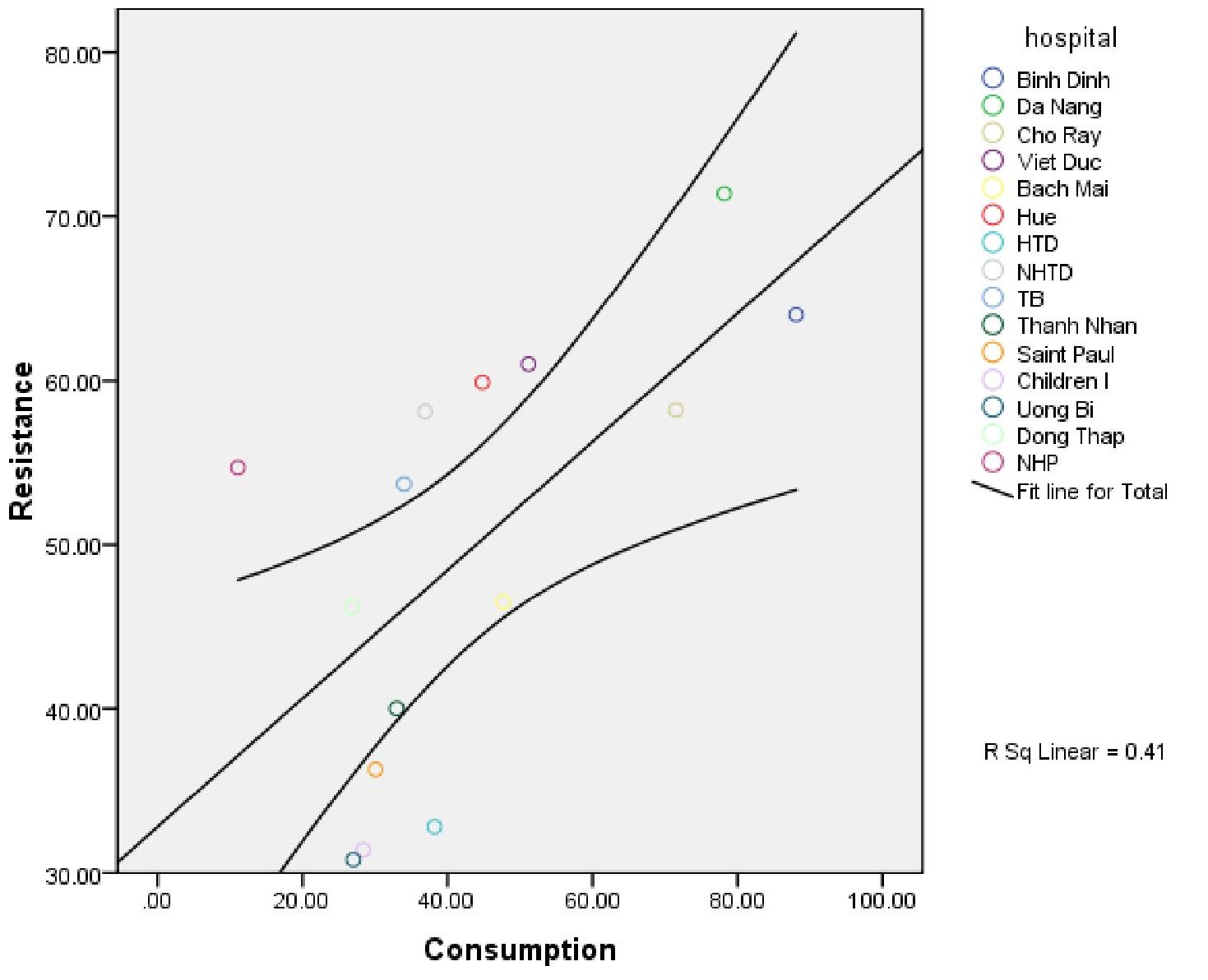
Tăng sử dụng cephalosporin, gia tăng kháng của E coli
1-1-1990 đến 31-8-2012
Nguyen et al. BMC Public Health 2013, 13:1158 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/13/1158

Các cơ chế kháng KS của vi khuẩn gram âm
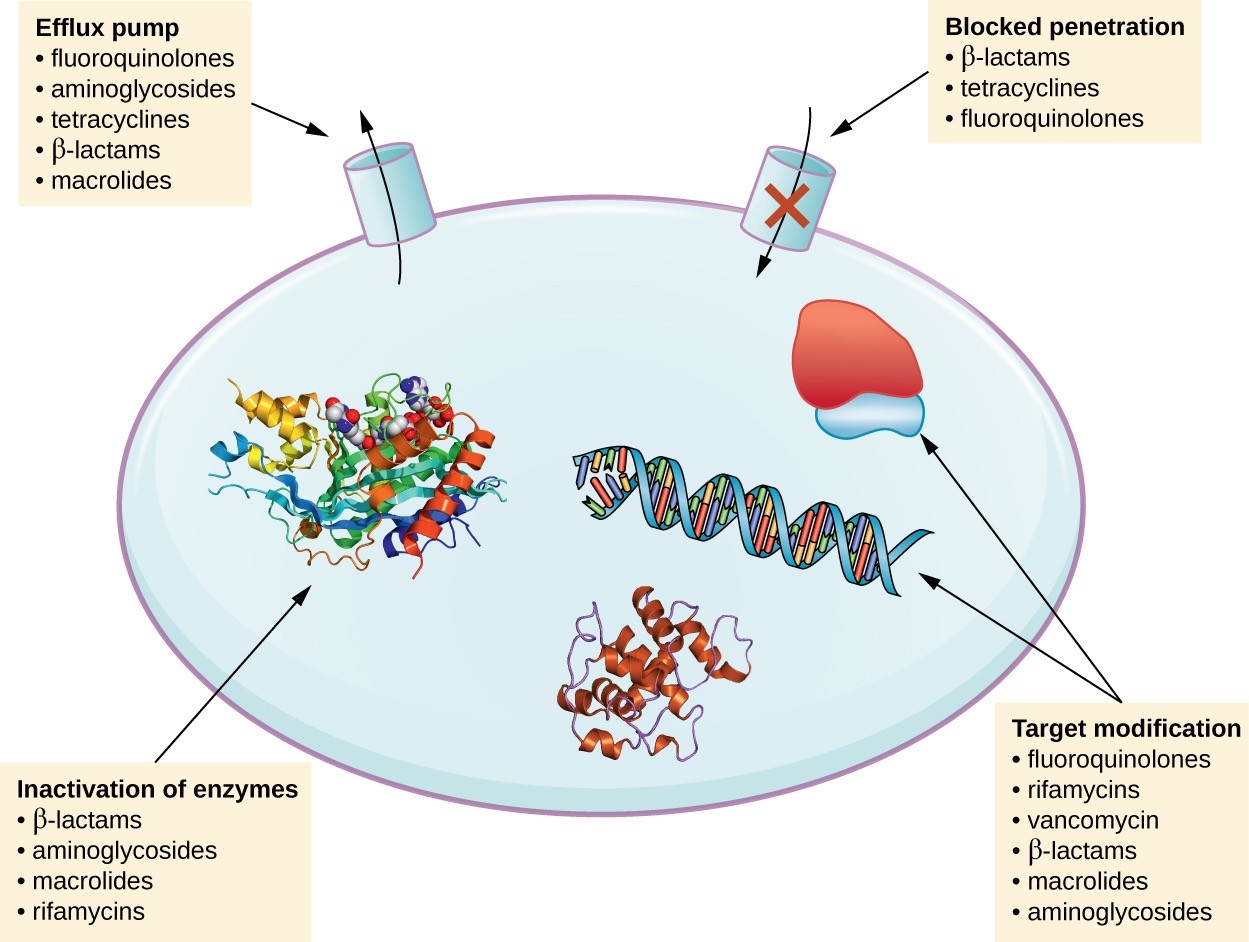
An overview of the antimicrobial resistance mechanisms of bacteria. AIMS Microbiol. 2018; 4(3): 482–501. doi: 10.3934/microbiol.2018.3.482
Enterobacteriaceae
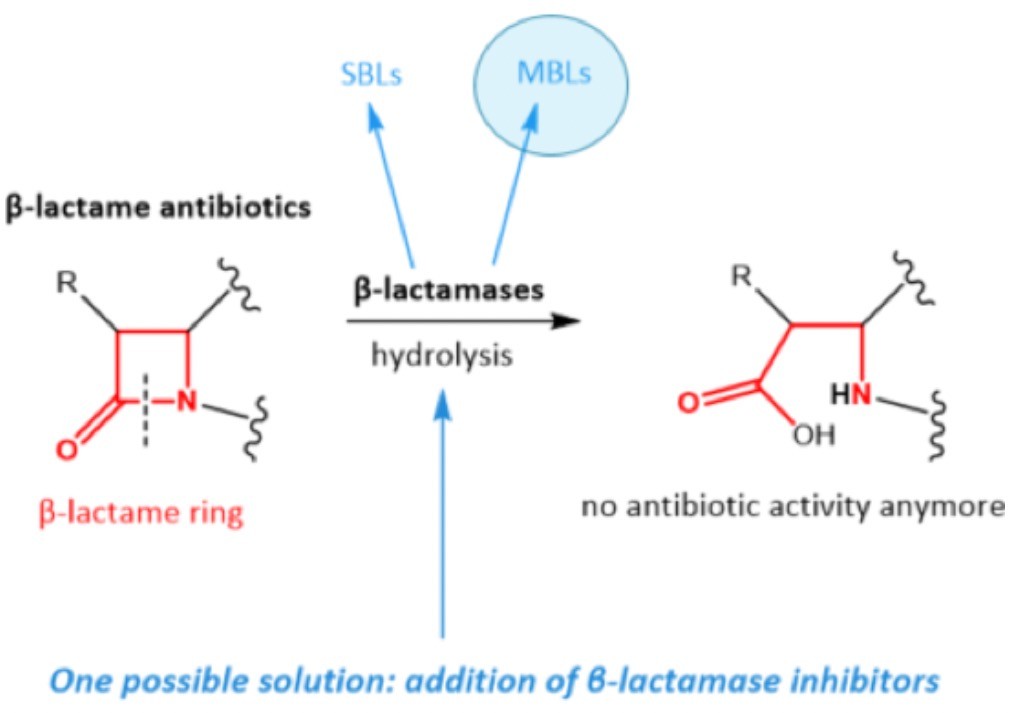 Tiến hoá của β-lactamases
Tiến hoá của β-lactamases
2 nhóm này hoạt động thuỷ phân theo 2 con đường khác nhau.
Table 1.2. Functional classification of β-lactamases according to the Ambler system.
β-lactamase type Ambler sub-class Examples
Phân loại khác:
- β-lactamases phổ hẹp: PNC, cepha thế hệ 1,2
- β-lactamases phổ rộng: (ESBL): tất
cả trừ carbapenem
- Carbapenemase
Serine β-lactamases
Metallo-β-lactamases (Class B)
Class A TEM-1, SHV-1, KPC-2
Class C DHA-1, CMY-1
Class D OXA-48
Class B1 NDM-1, IMP-1, VIM-2
Class B2 CphA, SFH-1
Class B3 GOB-11, L1

Understanding the evolution and biogenesis of the β-lactamase superfamily in Enterobacteriaceae, Doctor of Philosophy at Monash University in October 2022
 Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
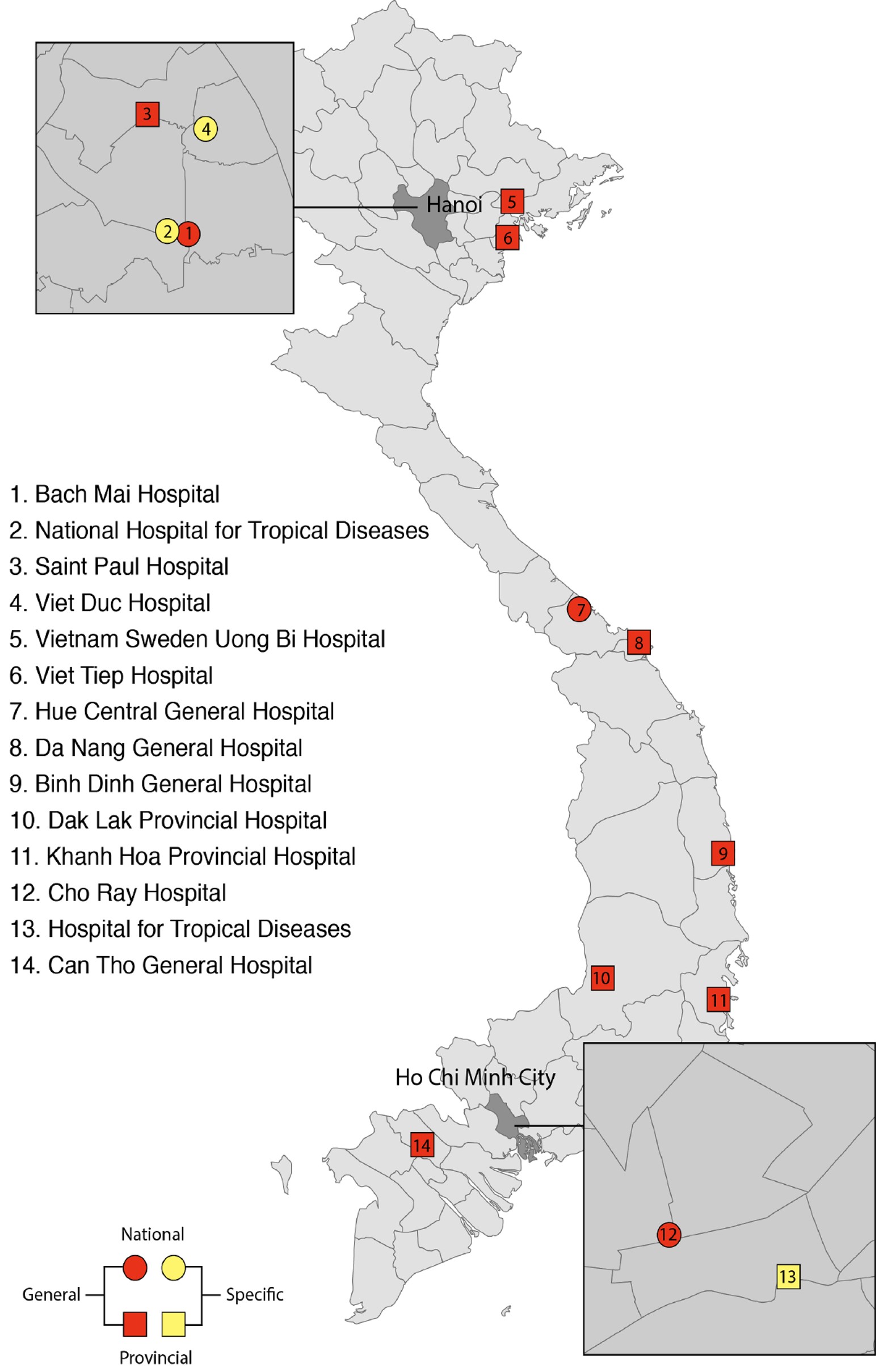
ESBL tại Việt Nam
| Hospital | E. coli | Klesiella sp. |
| Bach Mai | 18.0 (175/970) | 3.0 (3/99) (isolated from blood) |
| NHTD | 54.7 (64/117) | 72.7 (176/242) |
| NHP | 37.6 (146/388) | 51.3 (294/573) |
| TB | 23.4 (11/47) | 7.0 (21/298) |
| Viet Duc | 57.3 (63/110) | 48.5 (16/33) |
| Saint Paul | 31.7 (52/164) | 41.2 (42.102) |
| Thanh Nhan | 41.2 (7/17) | 12.5 (1/8) |
| Hue | 33.9 (103/304) | 37.5 (69/184) |
| Da Nang | 23.9 (112/468) | 13.2 (58/438) |
| Binh Dinh | 35.8 (210/586) | 54.3 (227/418) |
| Children I | 38.1 (275/722) | 54.1 (392/724) |
| Dong Thap | 14.7 (78/531) | 25.0 (56/224) |
| Cho Ray | 49.0 (25/51) | 58.2 (139/239) |
| HTD | 34.8 (24/69) | 20.5 (9/44) |
100
090
080
070
060
050
040
030
020
010
000
Global Antibiotic Resistance Partnership – Vietnam, 2008
2022 2023
6 tháng/2023, BVNĐ1, n =181
Enterobacteriaceae
ESBL
Blood stream Infection (BSI)
Countries K. pneumoniae E. coli
| Mean | Range | Mean | Range | ||
| Indonesia | Ceftriaxon | 73.5 | 68.0–78.3 | 72.3 | 67.0–76.7 |
| Ceftazidime | 69.4 | 64.0–74.8 | 58.7 | 53.0–64.3 | |
| Cefotaxime | 80.0* | 68.0–88.2* | 87.3 | 78.0–93.2 | |
| Malaysia | Ceftriaxon | 33.3 | 31.0–35.3 | 25.5 | 24.0–27.3 |
| Ceftazidime | 33.1 | 32.0–34.3 | 18.5 | 18.0–19.5 | |
| Cefotaxime | 35.3 | 34.0–36.6 | 27.3 | 26.0–28.5 | |
| Phillippines | Ceftriaxon | 55.1 | 52.0–57.8 | 33.8 | 31.0–36.6 |
| Ceftazidime | 50.8 | 48.0–53.6 | 26.2 | 24.0–28.8 | |
| Cefotaxime | 57.6 | 54.0–61.1 | 40.7 | 37.0–44.7 | |
| Thailand | Ceftriaxon | 27.9 | 24.0–32.3 | 36.1 | 33.0–39.0 |
| Ceftazidime | 29.6 | 25.0–34.3 | 19.3 | 17.0–21.9 | |
| Cefotaxime | 27.7 | 24.0–32.2 | 36.8 | 34.0–39.9 | |
| Myanmar | Ceftriaxon | 80.0 | 58.0–91.9 | 82.1 | 67.0–91.0 |
| Ceftazidime | NA | NA | 75.0 | 53.0–88.8 | |
| Cefotaxime | 92.9 | 69.0–99.6 | 77.4 | 60.0–88.6 | |
| Laos | Ceftriaxon | 30.6 | 18.0–46.9 | 45.9 | 37.0–55.2 |
| Ceftazidime | 76.9 | 50.0–91.8 | 44.6 | 33.0–56.7 | |
| Cefotaxime | NA | NA | NA | NA | |
Table 4
2012
Prevalence (%) of extended-spectrum β-lactamase-producing Enterobacteriaceae. Country ICU isolates Non-ICU isolates All isolates
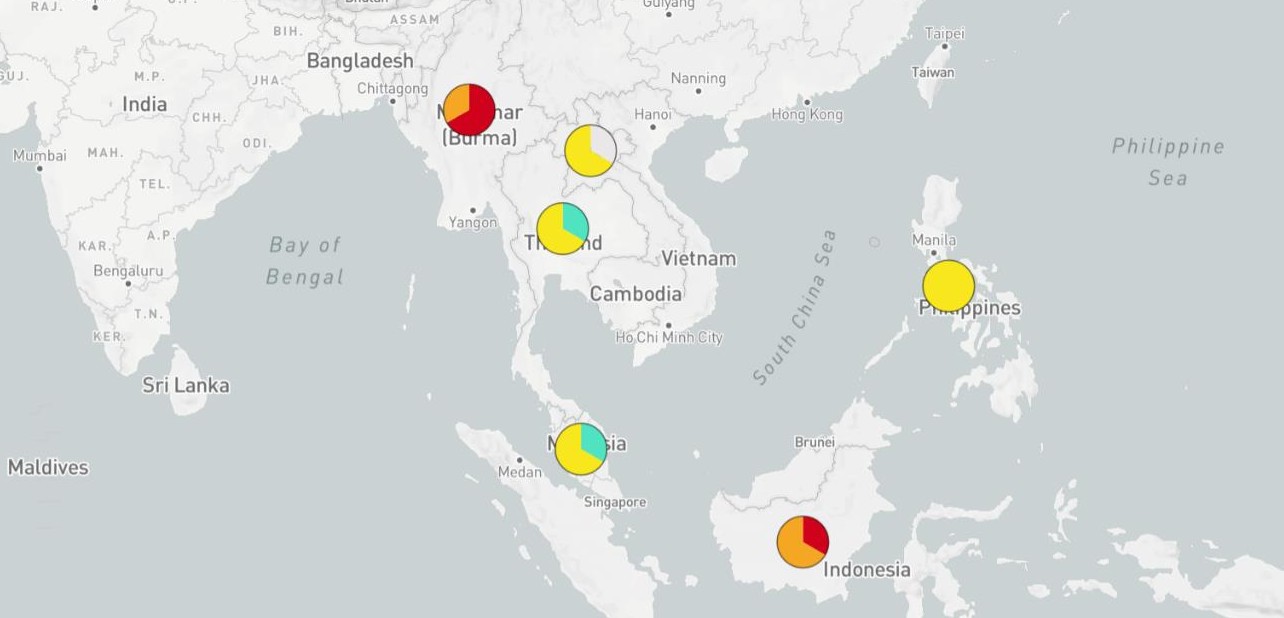
| New Zealand | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Philippines | 58.8 | 27.5 | 36.8 |
| Singapore | 17.2 | 21.2 | 19.8 |
| Thailand | 44.4 | 45.3 | 45.2 |
| Vietnam | 81.0 | 43.8 | 55.1 |
| Overall | 43.8 | 37.6 | 39.4 |
 ICU, Intensive Care Unit.
ICU, Intensive Care Unit.
Kiratisin P, COMPACT II study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012 Apr;39(4):311-6.
Sunaíno S, et al. Extended spectíum beta lactamase (ESBL)- píoducing Escheíichia coliand Klebsiella pneumoniae in Indonesia and South East Asian countíies: GLASS Data 2018. AIMS Micíobiol. 2023.
2018

Pseudomonas aeruginosa và Acinetobacter baumannii
| Nước | P aeruginosa | A. baumannii | Gr âm khác |
| New Zealand P | 10.3 | – | 12.5 |
| Philippines | 31.1 | 25.0 | 2.9 |
| Singapore | 23.3 | 90.5 | 4.2 |
| Thailand | 28.7 | 76.3 | 0.4 |
| Vietnam | 46.7 | 89.5 | 5.6 |
BV NĐ1, 2023
P aeruginosa kháng carbapenem 35%
A baumannii kháng carbapenem 77%
Kiratisin P, COMPACT II study. Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2012 Apr;39(4):311-6.
 Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
Nguyên tắc điều trị
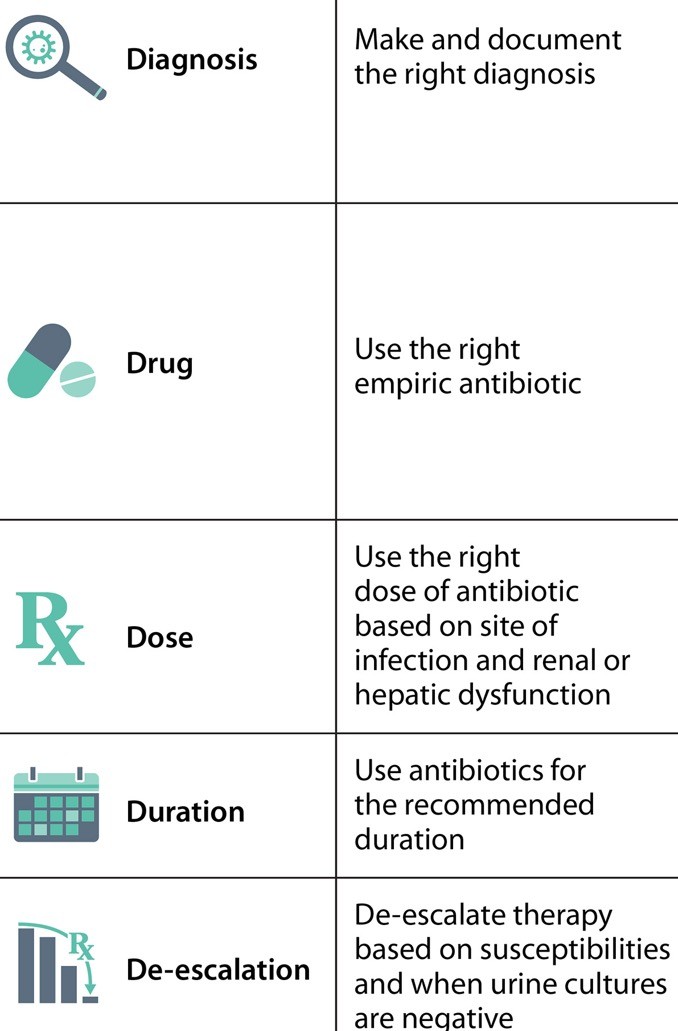
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/CMR.00003-20
 Enterobacteriaceae
Enterobacteriaceae
Chọn kháng sinh kháng carbapenem
| CRAB | ESBLs | CRPA
non-MBL |
CRE
non-CP |
CRE-KPC | CRE-OXA-48 | CRE-MBL | |
| New antibiotics
Ceftolozane-tazobactam |
No | Yes | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| Ceftazidime-avibactam | No | Yes | Yes | þ/e | Yes | Yes | No |
| Meropenem-vaborbactam | No | Yes | No | þ/e | Yes | No | No |
| Imipenem-cilastatin/ relebactam | No | Yes | Yes | þ/e | Yes | No | No |
| Plazomicin Eravacycline Cefiderocol | No Yes Yes | Yes Yes Yes | þ/e No Yes | Yes Yes Yes | Yes Yes Yes | Yes Yes Yes | þ/e Yes Yes |
| Old antibiotics
Polymyxins |
Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Aminoglycosides | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e |
| Fosfomycin iv | No | Yes | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e | þ/e |
| Aztreonam | No | No | þ/e | No | No | No | þ/e |
| Tigecycline | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Temocillin | No | Yes | No | No | þ/e | No | No |
M. Paul et al. / Clinical Microbiology and Infection 28 (2022) 521e547
Ceftazidime- Avibactam Trẻ từ 3 tháng

Các hướng dẫn điều trị
-
- Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
- M. Paul et al. / Clinical Microbiology and Infection 28 (2022) 521e547
- Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of infections caused by carbapenem- resistant gram-negative bacilli. China 2023
- Indian 2022: Guidance on Diagnosis & Management of Carbapenem Resistant Gram-negative Infections
- Nhiễm khuẩn tiết niệu ESBL-E
Enterobacterales sinh ESBL
 Viêm bàng quang không biến chứng TMP- SMX, Nitrofuratoin (hiệu quả) Levo, Cipro, carbapenem
Viêm bàng quang không biến chứng TMP- SMX, Nitrofuratoin (hiệu quả) Levo, Cipro, carbapenem
1 liều AG
Viêm đài bể thận
Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin hay TMP- SMX Carbapenem hay AG (đủ liều)
Nitrofuratoin không đủ nồng độ thuốc trong thận
- Không dùng Amox-a Clav vì tỷ lệ thành công thấp, thay đổi vi khuẩn thường trú
- Doxycyline không có bằng chứng
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2022 Guidance on the Treatment of Extended-Spectrum β- lactamase Producing Enterobacterales (ESBL-E), Carbapenem-Resistant Enterobacterales (CRE), and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with Difficult-to-Treat Resistance (DTR-P. aeruginosa). Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Aug 25;75(2):187-212. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciac268. PMID: 35439291; PMCID: PMC9890506.
Nhiễm khuẩn ngoài tiết niệu ESBL-E
Enterobacterales sinh ESBL
Carbapenem (mero, Imi, erta)
Nặng hay giảm albumin (2,5)
-
- Meropenem
- Imipenem
Erta gắn albumin cao, giảm alb làm giảm nồng độ thuốc, tử vong tăng 5 lần

Sau đó có thể xuống thang bằng Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin hay Trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole
Không
- Cefepime: ESBL phá huỷ, test không chính xác
- PIP/TAZO: Tazo hiệu quả
giảm, tử vong cao
- Beta lactam/chat ức chế: dành cho đa kháng
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
Điều kiện xuống thang: Nhạy, ổ nhiễm kiểm soát, huyết động ổn, hấp thu tốt
- Nhiễm trùng đường tiểu do Gram âm kháng carbapenem (CRE)
CRE

Viêm bàng quang không biến chứng
TMP- SMX, Nitrofuratoin, Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin,
Colistin, AG 1 liều
Viêm đài bể thận
Levofloxacin, Ciprofloxacin hay TMP- SMX, AG
Ceftazidime- avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam, cefiderocol
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

Nhiễm trùng ngoài đường tiểu Gram âm kháng carbapenem
CRE không có thực hiện được test carbapenemase
Ceftazidime-avibactam, meropenem-vaborbactam, và imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam
Nghi metallo: Cefiderocol hay Cef/avi+ Atreonam
Carbapenemase: blaKPC (86%)
- Ceftazidime-avibactam có hoạt tính hầu hết KPC-và OXA48
- Meropenem-vaborbactam & imipenem-cilastatin-relebactam KPC, không OXA-48
- Tất cả không có tác dụng metallo-β- lactamase (NDM)
“Ceftazidime-avibactam không có hoạt tính trên các chủng sinh men metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)”
ESCMID 2022:
- không có bằng
chứng
imipenem-cilastatin-
relebactam
- Khi kháng tất cả: Cefiderocol
- Khi kháng đơn trị: Cef-avi+ aztreonam
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

Cơ chế kháng của vi khuẩn gram âm
Meropenem- vaborbactam, Imipenem-cilastatin- relebactam chỉ KPC
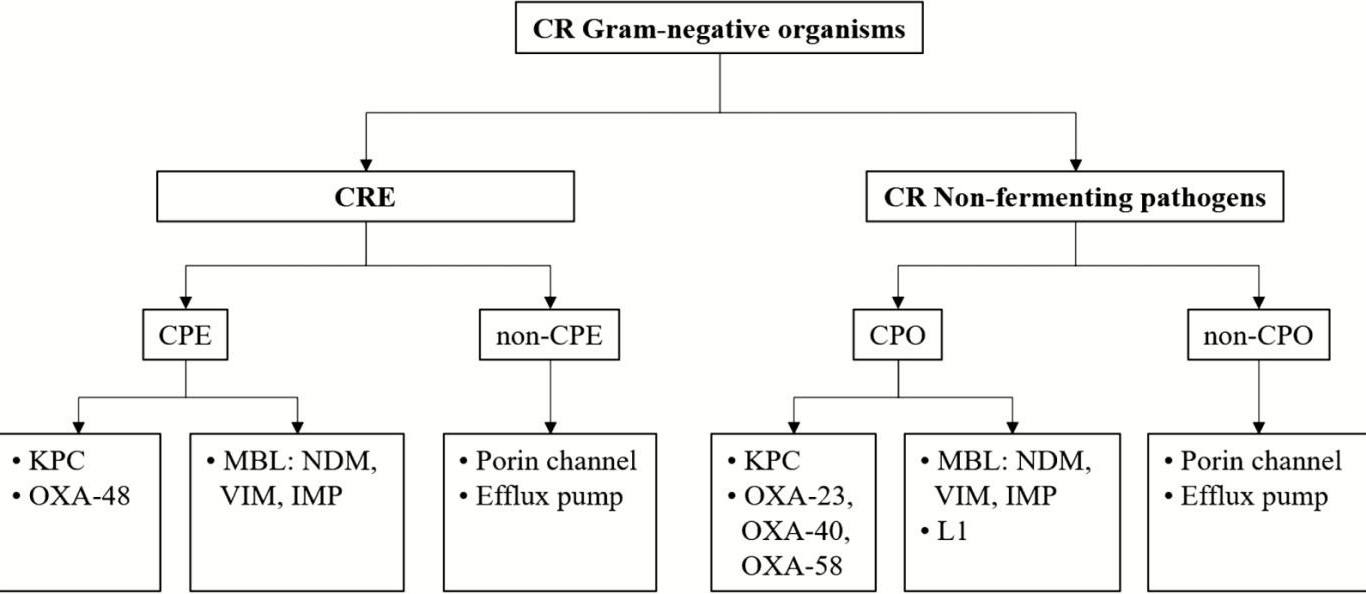
Ceftazidime- avibactam cả KPC và OXA48
Nhiễm trùng ngoài đường tiểuGram âm kháng carbapenem
Gram âm đa kháng
KPC
Metallo-β-lactamase
NDM
OXA48 CRE
-
- Ceftazidim-avibactam 2.Cefiderocol
- Mero/vabo và Imi/rele
không hoạt OXA48
tính
với
- Ceftazidim- avibactam + aztreonam
- Cefiderocol
Theo thứ tự khuyến cáo
- Meropenem- vaborbactam
- Ceftazidime-
avibactam,
- Imipenem-cilastatin- relebactam
- Cefiderocol
Khi không còn thuốc khác:
- Tigecycline 2.Eravacycline Không dùng NTH và NT tiểu (vào mô nhanh), liều cao

Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
- NDM không thuỷ phân aztreonam
- Atreonem lại bị phân huỷ
bởi khác
các
carbapenemase
Tỷ lệ chửa khỏi (85%), tử vong (12%) và kháng thấp nhất với mero/vabo

Nhiễm trùng Gram âm kháng carbapenem
Question 3.10: What is the role of polymyxins for the treatment of infections caused by CRE?
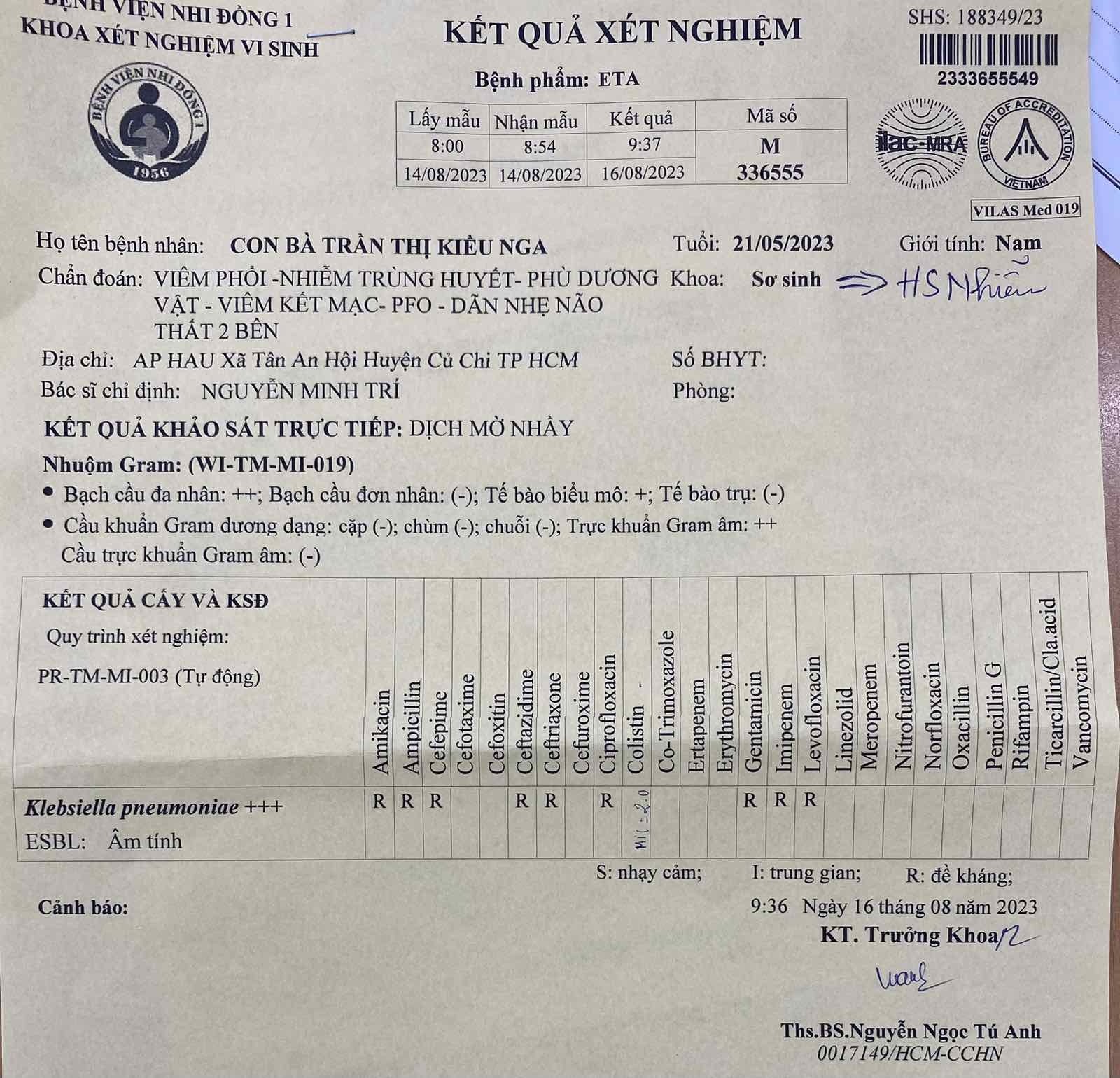
- 2 tháng 25 ngày, Nằm viện từ lúc sanh
- Viêm phổi thở máy tại BV.
- Kết quả kháng sinh đồ
- Điều trị: Meropenem + Colistin
Suggested approach: Polymyxin B and colistin are not suggested for the treatment of infections caused by CRE. Colistin can be considered as an alternative agent for uncomplicated CRE cystitis.
“Ceftazidime-avibactam không có hoạt tính trên các chủng sinh men metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)”
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

Nhiễm trùng Gram âm kháng carbapenem
Vi khuẩn Gram-âm đa kháng: Colistin kết hợp với carbapenem, fluoroquinolon, rifampicin
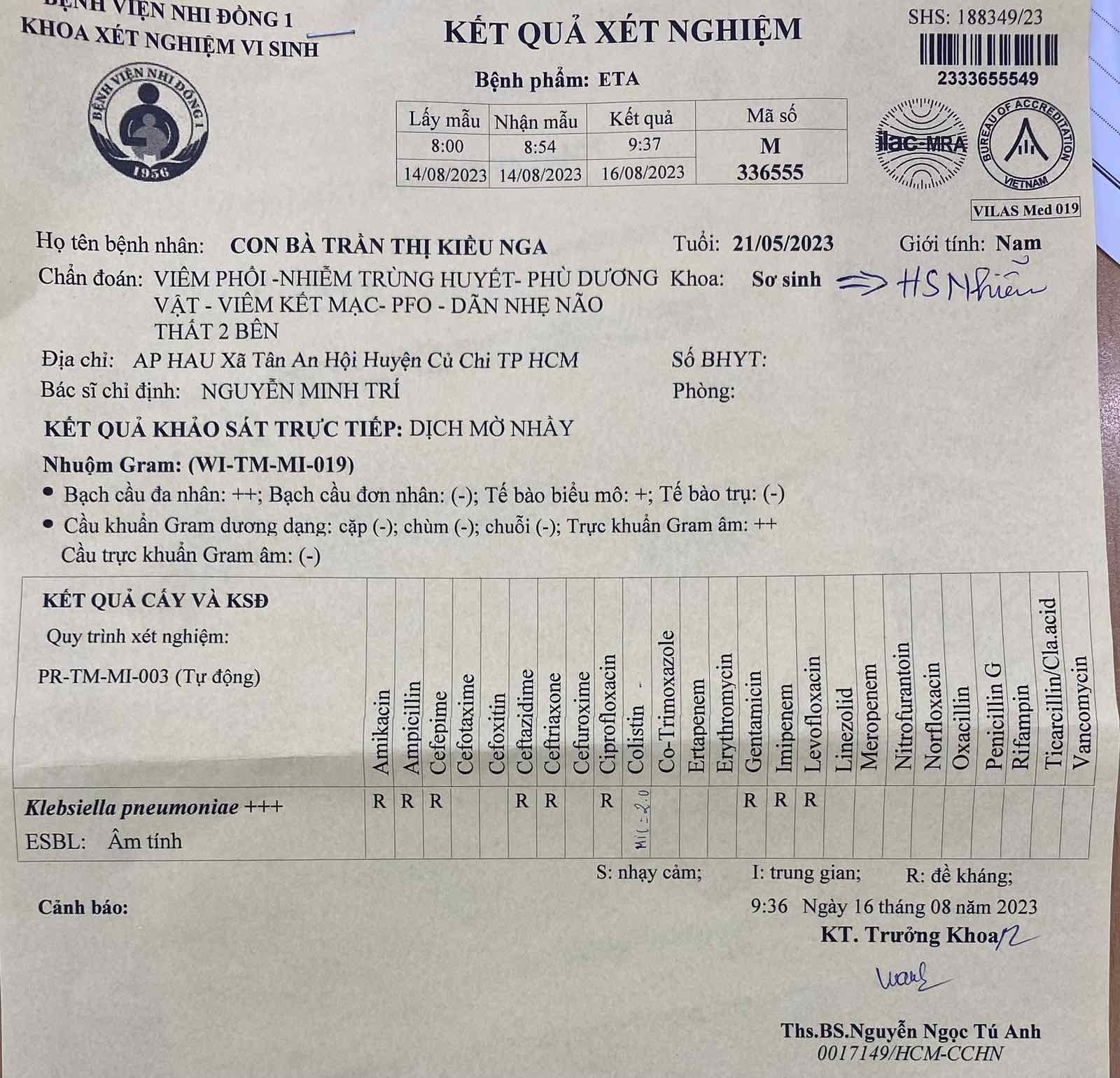
- 2 tháng 25 ngày, Nằm viện từ lúc sanh
- Viêm phổi thở máy tại BV.
- Kết quả kháng sinh đồ
- Điều
Colistin
trị:
Meropenem
+
Hướng dẫn sử dụng kháng sinh
(ban hành kèm theo quyết định số 708/QĐ-BYT ngày 02/3/2015)
Question 3.11: What is the role of combination antibiotic therapy for the treatment of infections caused by CRE?
Suggested approach: Combination antibiotic therapy (i.e., the use of a β-lactam agent in combination with an aminoglycoside, fluoroquinolone, tetracycline, or polymyxin) is not suggested for the treatment of infections caused by CRE.
“Ceftazidime-avibactam không có hoạt tính trên các chủng sinh men metallo-β-lactamase (MBL)”
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

CRE: colistin + Meropenem là lựa chọn cuối cùng
-
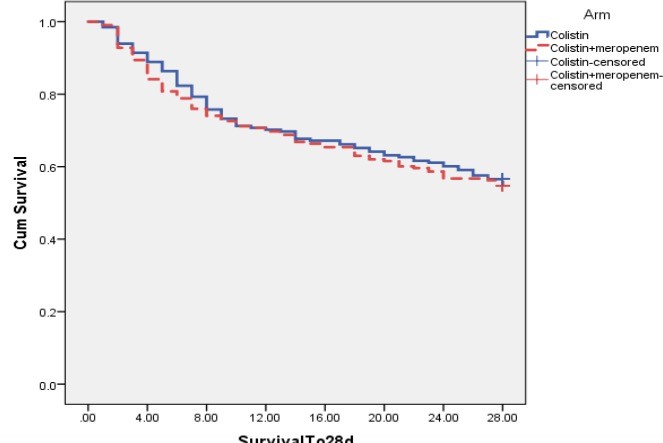 2016-2018, châu Âu
2016-2018, châu Âu- 198 BN colistin (9 triệu Đv, 4,5 mỗi 12 giờ: 43,4%
- 208 BN, Meropenem 2 g mỗi 8 giờ 45,2%
- Đơn trị với Colistin:
- Nồng độ thuốc thay đổi, khó đạt ngưỡng điều trị
- Liều cao đạt ngưỡng gần với liều độc thận
- Khổng đủ nồng độ thuốc trong phổi
- Kháng colistin đã ghi nhận
Paul M, Daikos GL, Durante-Mangoni E, Yahav D, Carmeli Y, Benattar YD, et al. Colistin alone versus colistin plus meropenem for
treatment of severe infections caused by carbapenem-resistant Gram-negative bacteria: an open-label, randomised controlled trial.
Lancet Infect Dis. (2018) 18:391–400. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(18)30099-9

CRE: kết hợp Colistin và carbapenem
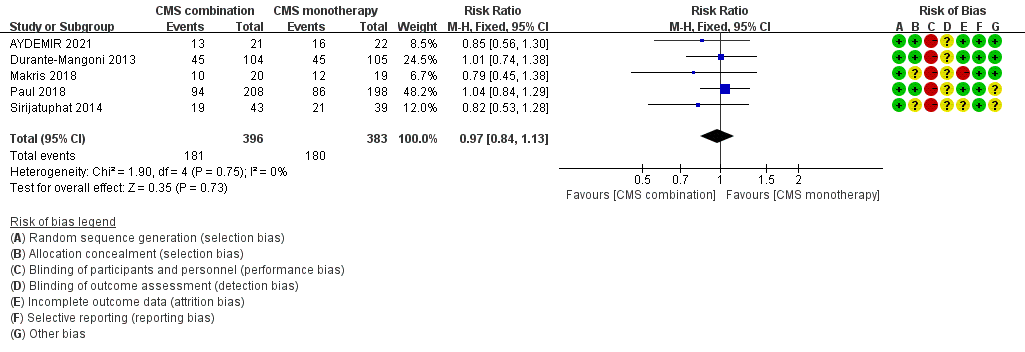
Tử vong
PICO question 4. should polymyxin combination therapy be preferred over polymyxin monotherapy for treatment of CRGNB infections?
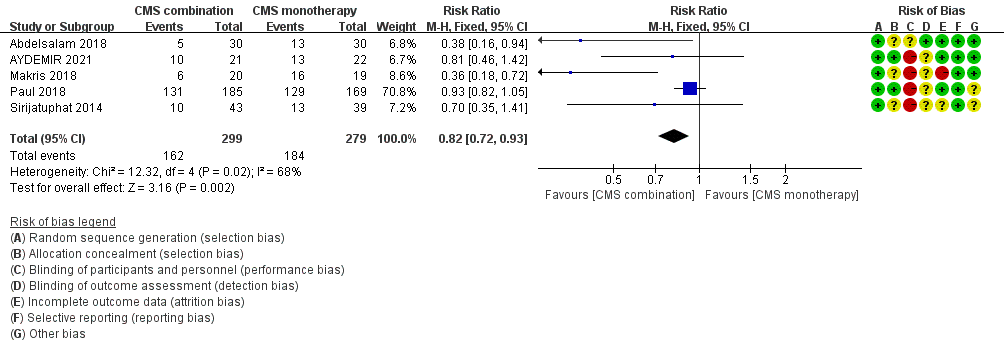
Cải thiện LS
-
- Recommendation: Polymyxin combination therapy is recommended as a preferential choice over monotherapy for treating CRGNB infections in patients who requires polymyxin treatment (strong recommendation, moderate- quality evidence).
- Polymyxin và carbapenem khi CRGNB nếu meropenem MIC <8 mg/L với CRE và 32 mg/L với CRAB.
- Recommendation: Polymyxin combination therapy is recommended as a preferential choice over monotherapy for treating CRGNB infections in patients who requires polymyxin treatment (strong recommendation, moderate- quality evidence).
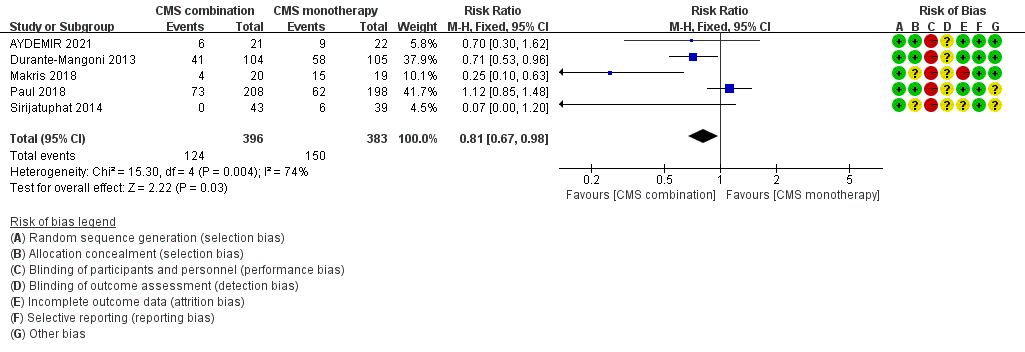
Sạch khuẩn
Guidelines for the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control of infections caused by carbapenem-resistant gram-negative bacilli. China 2023
 Figure 12-1. Enteric Bacilli: Bacilli and Pseudomonas With Known Susceptibilities (See Text for Interpretation)
Figure 12-1. Enteric Bacilli: Bacilli and Pseudomonas With Known Susceptibilities (See Text for Interpretation)
Tier 1
Ampicillin IV (amoxicillin PO)
Tier 2
Trimethoprim/sulfamethoxazole IV and PO
Cephalosporin (use the lowest generation susceptible)
- First: cefazolin IV (cephalexin PO)
- Second: cefuroxime IV and PO
- Third: cefotaxime/ceftriaxone IV (cefdinir/cefixime PO)
- Fourth: cefepime IV (no oral fourth generation)
Tier 3
Carbapenem IV (no PO)
- Meropenem/imipenem IV
- Ertapenem IVa,b
Aminoglycoside IV (no PO)
- Gentamicin IV
- Tobramycin IV
- Amikacin IVa,b
Combination beta- lactamase inhibitor
- Piperacillin/ tazobactam IV (no PO)b
Tier 4
Ceftazidime/avibactam IV (no PO) (for carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella)c
Tier 5
Tier 6
Abbreviations: ESBL, extended-spectrum beta-lactamase; IV, intravenous; PO, orally; SPICE, Serratia, indole-positive
Proteus, Citrobacter, Enterobacter.
Polymyxins: colistin IV (no PO)
Fluoroquinolone: ciprofloxacin IV and POb,d
ESBL-carrying bacilli considered resistant to all third- and fourth-generation cephalosporins
-AmpC inducible SPICE pathogens and Pseudomonas usually susceptible to cefepime (fourth generation) but resistant to third generation
Approach to Antibiotic Therapy for Drug-Resistant Gram-negative Bacilli & MRSA
12
HO O P
O
OH
Updates available at www.aap.org/
Nelsons
John D. Nelson, MD
Emeritus
Elizabeth D. Barnett, MD Joseph B. Cantey, MD, MPH David W. Kimberlin, MD Paul E. Palumbo, MD
Jason Sauberan, PharmD
J. Howard Smart, MD William J. Steinbach, MD Contributing Editors
Nelson’s Pediatric Antimicrobial Therapy
29th Edition
John S. Bradley, MD
Editor in Chief
2023

4. P. aeruginosa kháng thuốc khó điều trị
DTR(2018): Kháng hết tất cả KS piperacillin-tazobactam, ceftazidime, cefepime, aztreonam, meropenem, imipenem-cilastatin, ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin.
Difficult to treat resistance (DTR): Resistance to all b-lactams, including carbapenems, b- lactamase inhibitor combinations and fluoroquinolones
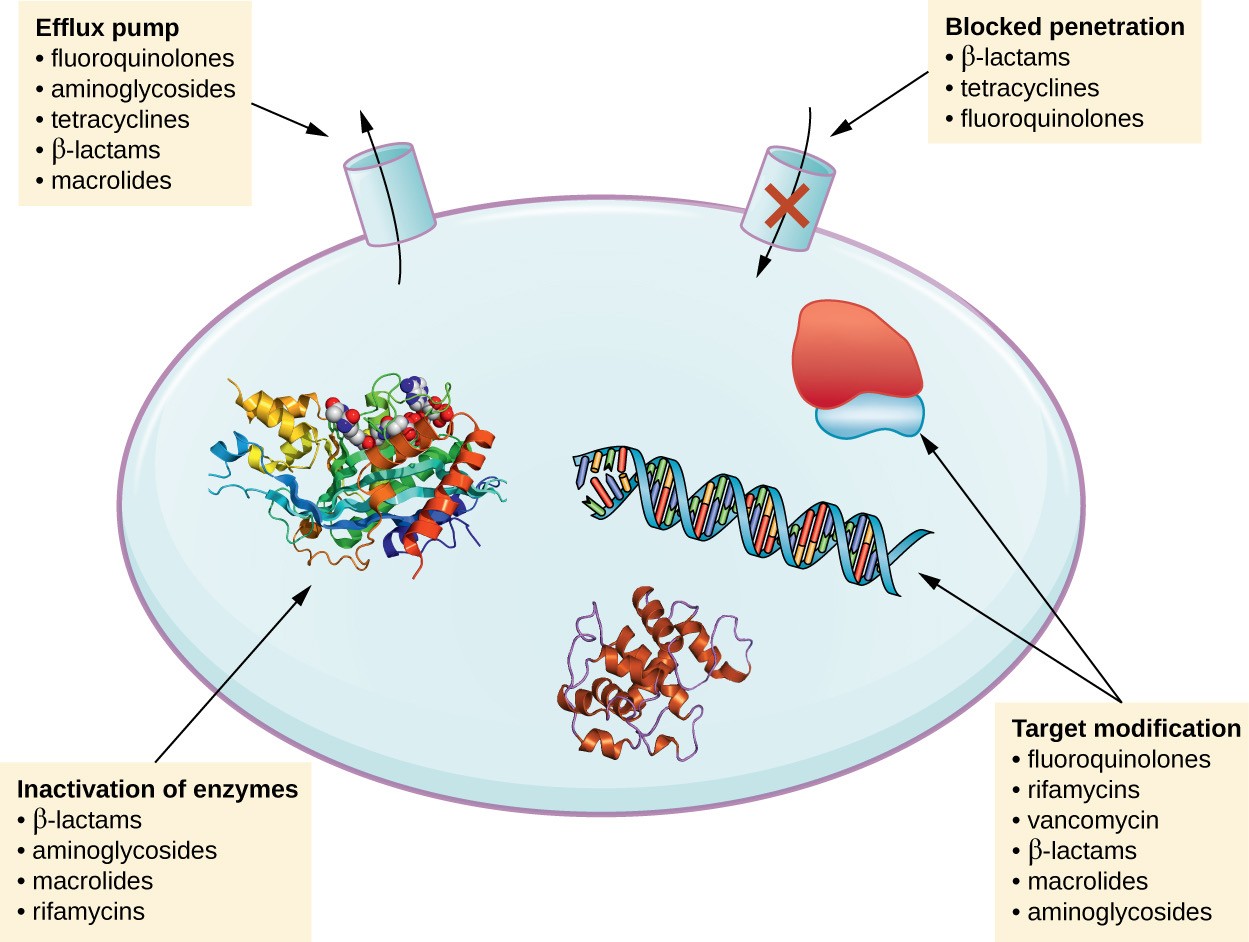
Carbapenemase (BlaVIM)
Guiana extended-spectrum beta- lactamase Vietnamese extended-spectrum beta- lactamase [VEB]
ESBL
(Blaoxa10) AmPC
Bơm ra ngoài (Mex AB porrM
Giảm tinh thấm
Thay đổi PBP
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
P. aeruginosa kháng thuốc khó điều trị
20% – 60% P. aeruginosa kháng carbapenem, nhưng nhạy b- lactam khác
P. aeruginosa kháng thuốc/ kháng khó điều tíị
Còn nhạy β-lactam, Quinolone, carbapenem: dùng thuốc này liều cao, truyền kéo dài
Metalo-beta lactamase:
Cefiderocol
Ceftolozane-tazobactam, ceftazidime-avibactam, imipenem-cilastatin- relebactam, Cefiderocol
 ESCMID 2022: Ceftolozane-tazobactam
ESCMID 2022: Ceftolozane-tazobactam
Không có vai trò của KS khí dung
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

- Carbapenem Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Treatment Options
-
- Use a β-Lactam (ceftazidime or cefepime) or β-lactam-β-lactamase inhibitor combination (piperacillin-tazobactam or cefoperazone- sulbactam) if in-vitro susceptibility is demonstrated
- Aminoglycosides (if in-vitro susceptibility is demonstrated)
- Polymyxins (for infections in which no other treatment option is available)
- For patients with severe infections caused by CRPA susceptible in vitro only to polymyxins, aminoglycosides, or fosfomycin, a combination therapy is suggested. Polymyxins plus other agent to which organism has demonstrated susceptible MIC or in intermediate range or SDD (susceptible dose dependent) can be used in such scenario. (Consultation with an Infectious Disease Physician or a physician having experience in treating such infections is advised)
Indian 2022: Guidance on Diagnosis & Management of Carbapenem Resistant Gram-negative Infections

CRAB
Khó khăn với CRAB:
-
- Tạm trú tại đường hô hấp, đo đó phân lập được không chắc tác nhân gây bệnh hay tạm trú tại đây.
CRAB kháng carbapenem gần như kháng hết các KS hiện nay, đo đó chọn lựa khó khăn.
-
-
- Kháng tạo: OXA carbapenemases (OXA- 24/40, OXA-23), metallo-β-lactamases, serine carbapenemases (e.g., Acinetobacter baumannii– derived cephalosporinases)
- Kháng Aminoglycoside: qua methyltransferases
- Kháng quinolone qua các đột biến của NST
-
Chưa có phác đồ chuẩn nào hiệu qủa với CRAB
CRAB: không có 1 phác đồ đơn trị nào
- Tiếp cận điều trị: phối hợp ampicillin-sulbactam với ít nhất 1 thuốc khác
9. Khí dung Ks: không
- Phối hợp KS (polymyxin b, minocycline, tige,
cefiderocol): 2 KS cho đến
khi cải thiện
8.Rifampicin Không
5. Vai trò của dẫn xuất tetracycline: minocycline và tigecycline liều cao
CRA B
6. Cefiderocol
Khi kháng hay không dung nạp tất cả, phối hợp KS khác
7. Meropenem và Imipenem truyền kéo dài:
không
- Vai trò của ampicillin-sulbactam: liều cao là 1 thành phần của
điều trị, dù có kháng ampicillin
- Vai trò của Polymyxin: dùng kết hợp KS khác, không có lợi khi
MIC > 2,
 phối hợp 1 chất khác
phối hợp 1 chất khác
Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections
 4. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Question 4.1: What is the antibiotic of choice for CRAB? Recommendations
4. Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii Question 4.1: What is the antibiotic of choice for CRAB? Recommendations
For patients with CRAB susceptible to sulbactam and HAP/VAP, we suggest ampicillin-sulbactam (conditional recommenda- tion, low certainty of evidence).
●
For patients with CRAB resistant to sulbactam, a polymyxin or
●
high-dose tigecycline can be used if active in vitro. Lacking evi- dence, we cannot recommend on the preferred antibiotic.
We conditionally recommend against cefiderocol for the treat- ment of infections caused by CRAB (conditional recommen- dations against use, low certainty of evidence).
●
Clinical Microbiology and Infection 28 (2022) 521e547
Question 4.2: Should combination therapy be used for the treatment of CRAB?
Recommendations
For all patients with CRAB infections, we do not recommend polymyxin-meropenem combination therapy (strong recom- mendation against use; high certainty of evidence) or poly- myxin-rifampin combination therapy (strong recommendation against use, moderate certainty of evidence).
●
For patients with severe and high-risk CRAB infections, we suggest combination therapy including two in vitro active anti- biotics among the available antibiotics (polymyxin, amino- glycoside, tigecycline, sulbactam combinations) (conditional recommendation for use, very low certainty of evidence).
●
For patients with CRAB infections with a meropenem MIC <8 mg/L, we consider carbapenem combination therapy, using high-dose extended-infusion carbapenem dosing, as good clin- ical practice (good practice statement).
●

-
-
- Carbapenem Resistant Non- Enterobacterales (Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
- Carbapenem Resistant Acinetobacter baumannii (CRAB)
- Carbapenem Resistant Non- Enterobacterales (Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
-
Treatment Options
-
-
-
-
- High dose sulbactam (6-9g/day) on its own or as ampicillin-sulbactam (if susceptible) or cefoperazone-sulbactam (1g/1g).
- Polymyxins (use colistin instead of polymyxin B for UTI)
- Minocycline
- Tigecycline (do not use for UTI)
- Other agents like trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, aminoglycosides, if
-
-
-
susceptible Combination therapy with at least two active agents (include high dose sulbactam even if non-susceptible), whenever possible, is suggested for the treatment of moderate to severe CRAB infections
Indian 2022: Guidance on Diagnosis & Management of Carbapenem Resistant Gram-negative Infections
-
-
-
-
- S. maltophilia
-
-
-
Gen kháng thuốc: metallo β-lactamase, L2 serine β- lactamase
S. maltophilia
2 trong các kháng sinh sau:
TMP-SMX, minocyclin, tigecycline, levofloxacin cefiderocol
Phối hợp ceftazidime-avibactam và aztreonam

Không Ceftazidime “Ceftazidime-avibactam không có hoạt tính trên Stenotrophomonas maltophilia” Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023 Guidance on the Treatment of Antimicrobial Resistant Gram-Negative Infections

Thời gian điều trị
Table 6: Duration of therapy for common clinical syndromes
| Clinical Syndromes | Duration of therapy |
| Ventilator associated pneumonia or hospital acquired pneumonia | 7-10 days |
| Complicated urinary tract infections | 10 days |
| Catheter associated UTI | 5-7 days |
| Intra-abdominal infections | 4-7 days |
| Central line associated blood stream Infections | 10 ays |
*Removal of catheter or central line is strongly recommended if infection with an MDR organism is confirmed
Indian 2022: Guidance on Diagnosis & Management of Carbapenem Resistant Gram-negative Infections

Kết luận
MDRGN ngày càng nhiều, một phần lạm dụng hay dùng kháng sinh không phù hợp
Tối ưu việc dùng kháng sinh trong BV là quan trọng, cung cấp MIC và gen kháng
thuốc giúp cải thiện chọn lựa kháng sinh
Cần có các HD cập nhật cho sử dụng KS trong nhiễm gram âm đa kháng từng quốc gia hay đơn vị điều trị
Để lại một bình luận