A Year in Review Revised SSC Guidelines A Beacon of Light?
April 10, 2017
James D. Leo, MD, FACP, FCCP
Medical Director of Best Practice and Clinical Outcomes
Chair, Sepsis Best Practice Team MemorialCare Health System
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016?
- JAMA, Feb. 23, 2016: Sepsis-3, New criteria for defining sepsis

- Sepsis is redefined as : “life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection.”
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
- Organ Dysfunction: Rise in SOFA of ≥ 2 points
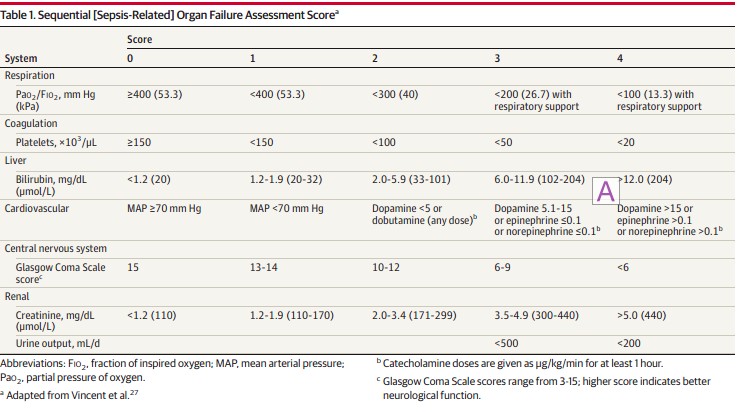

 Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
- Severe Sepsis: No longer used
- Sepsis:
- Suspected or documented infection and
 Acute increase of ≥2 SOFA points (a proxy for organ dysfunction)
Acute increase of ≥2 SOFA points (a proxy for organ dysfunction)
- Septic Shock:
- Sepsis and
- Vasopressor therapy needed to elevate MAP ≥65 mm Hg and
- Lactate >2 mmol/L (18 mg/dL) despite adequate fluid resuscitation
 Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
- qSOFA Score: A means of rapidly identifying ED and hospital ward (non- ICU) patients with suspected infection at increased risk


![]()
![]()
- At least 2 of 3 criteria:
- RR ≥ 22/min
- Altered mentation
- SBP ≤ 100 mmHg
 Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
The U.S. response to the new definition:

 Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? Sepsis-3
- U.S. professional societies didn’t adopt Sepsis-3 (ACEP, ACCP)


Chest May 2016
- CMS had already released SEP-1 Core Measure criteria based on Sepsis-2 definitions
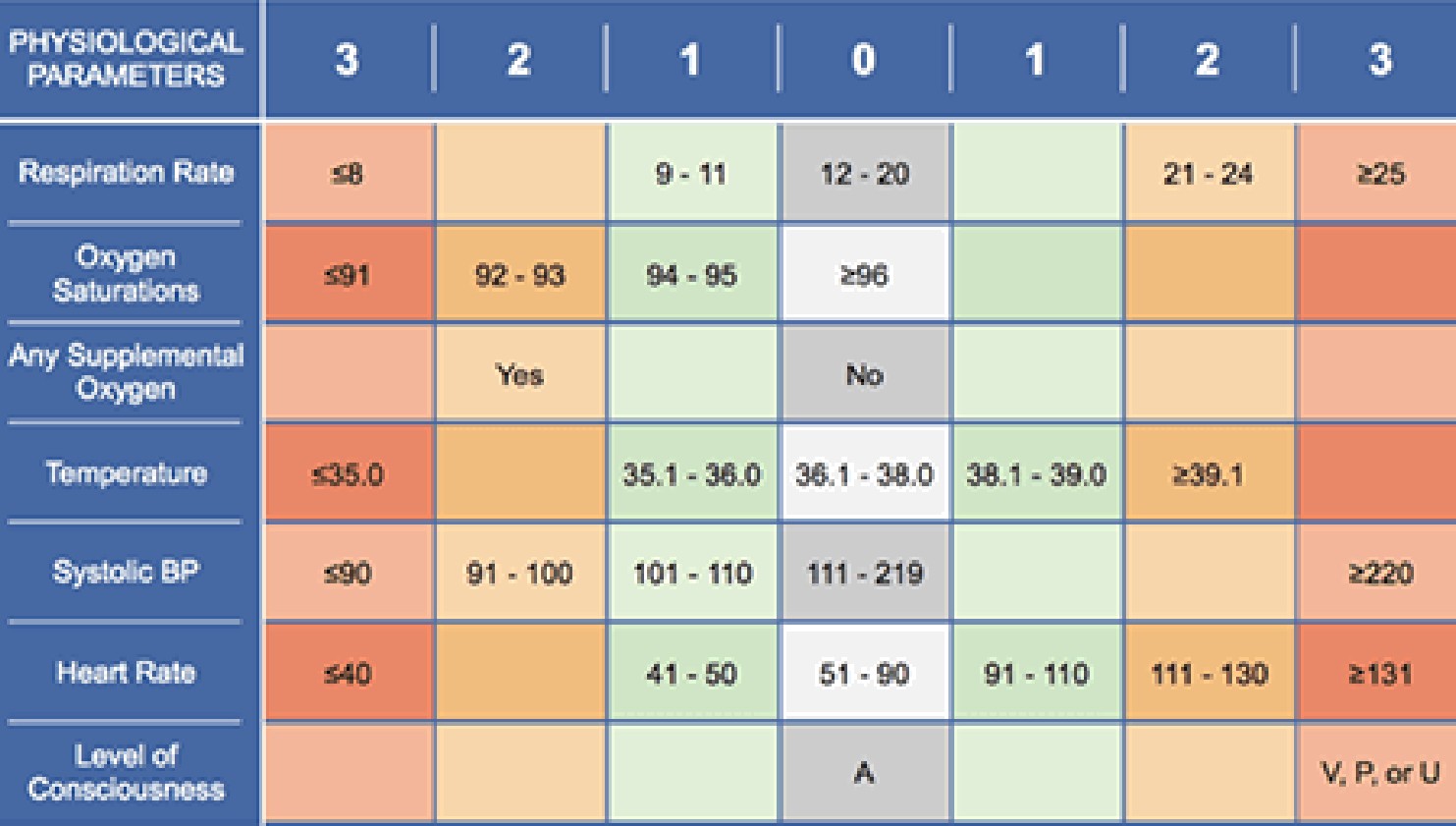
 How Good is SOFA?
How Good is SOFA?
JAMA 1/17/17

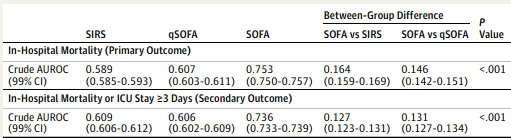
Conclusion: in the ICU, SOFA is better than SIRS or qSOFA

JAMA | Original Investigation | CARING F-OR THE CRITICALLY ILL PATIENT
Prognostic Accuracy of Sepsis-3 Criteria for In-Hospital Mortality Among Patients With Suspected Infection Presenting to the Emergency Department
Yonathan Freund, MD. PhD. Najla LemaÖiatti, MD. Evguenia Krastinova, MD, PhD: Marie Van Laer, MD. Yann-EnckClaessens, MD, PhD, Aurélie Avondo, MD; Céline Occelli, MD; Anne-Laure Ferai-Pierssens, MD;
Jennifer Tmchot. MD: Mar Drtega, MD. Bruno Carneiro, MD. Julie Pernet. MD: Rerre-Géraud Claret. MD. PhD;
Fabriœ Dami, MD. Ben Bloom, MD. Bmro Riou. MD, PhD: Sébastien Beaune. MD. PhD. farthe French Sooery of Ernergency Medicine Collaborators Group
Table Z. Diagnostic Performances forthe Pred’ætiori of In-Hospital Death
JAMA 1/17/17
| For Prediction of Oeath | qS0FA | SDFA | SIRS | ||
| Sensitivi\y, % (95a CI) | 70 (59-8d) | 73 (61•82) | 92 (85-98) | 47(36 59} | |
| Specific ivy, % (95% CI) | 79 (76-82) | 70 (67 -72) | 27 (24- J 1) | 82(80-B5) | |
| Prcdictive value, | (95% CI) | ||||
| Posit ise | 24 (1 830) | 18 (14-22) | 11 (8- IJ) | 20([4-27) | |
| h egat il e | 97 (95-98) | 97 /9s-98) | 98 (95-99) | 94(92-96) | |
| L ike ihood ratio (95s CI) | |||||
| Posit ise | J.40 (2.80-4.17) | 2.40 (2.00-2.90) | 1.2 9 (1.17 – L. 3 7) | 2.70 (2.00- 2.52) | |
| hegat ise | 0.J7 (0.3 6-g.52) | o.39 /o.›7-o.s6j | d.25 (0.1 1 -0.58) | 0.64 (g.51-0.79) | |
| AüROC. (9 5% CI) | 0.80 (0.74-0.85) | 0.7 7 (0.71-0.82) | g.65 (0.59-0.70) | o.6s /o.s9-o.7oj | |
 How Good is qSOFA?
How Good is qSOFA?


![]()
- Retrospective review of ED and ward patients with suspected infection
- Compared SIRS, qSOFA, MEWS, and NEWS
- Primary endpoint: in-hospital mortality, and combined endpoint of mortality or ICU admission
![]()
![]()
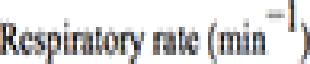
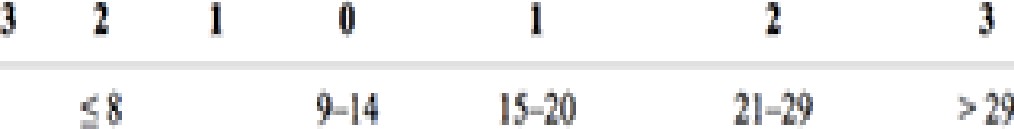

![]()

 Select cutoNs to predict mortality or ICU transfer
Select cutoNs to predict mortality or ICU transfer
| en ï | i | Specificity | |
| SIR5 z 2
q5OFA 2 2 |
9:t’¥•
|
67% |
|
| NEWS L 7 | 7796 | 53& | |
| NSWS z 8
NEWS 2 9 |
67&
5A96 |
66%
78B |
 How Good is qSOFA?
How Good is qSOFA?
Conclusions:
- qSOFA has a poor sensitivity
- qSOFA is a late indicator of deterioration
- qSOFA is inferior to the NEWS score (despite the NEWS score being based on data which is equally easy to obtain at the bedside)

 Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? VANISH Trial
Sepsis: What Happened in 2016? VANISH Trial
- Factorial 2 x 2 Design, DBRCT
| Vasopressin + Placebo
+/- Norepinephrine PRN |
Norepinephrine + Placebo
+/- Vasopressin PRN |
| Vasopressin + Hydrocortisone
+/- Norepinephrine PRN |
Norepinephrine + Hydrocortisone
+/- Vasopressin PRN |
Outcome: No difference in renal failure-free days.
No difference in mortality
 Statins in Sepsis
Statins in Sepsis

- Follow-up of patients from Statins for Acutely Injured Lungs from Sepsis (SAILS) Trial
- Compared rosuvastatin vs. placebo in patients with sepsis-induced ARDS
 Evaluated SF-36 physical function and mental health domains at 6 months
Evaluated SF-36 physical function and mental health domains at 6 months- Findings:
- No difference in 6-month survival
- No difference in physical function
- No difference in mental health
- No difference in 6-minute walk test
- “…survivors [demonstrated] substantial impairments in physical function and mental health.”
 Statins in Sepsis
Statins in Sepsis

- Another subgroup study from the SAILS Trial
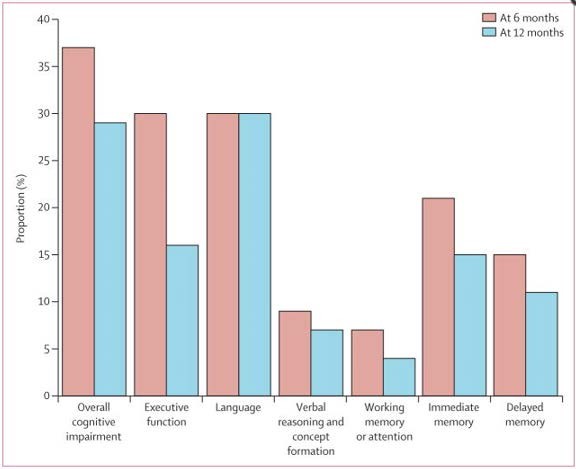 Evaluated impact of rosuvastatin on delirium
Evaluated impact of rosuvastatin on delirium- Findings:
- Most patients had delirium
– no between-group difference
-
- About 1/3 patients had cognitive impairment at 6 months
 Thiamine for Sepsis
Thiamine for Sepsis

- Thiamine 200 mg IV q12h vs. placebo x 7 days
- Endpoint: Lactate levels, time to shock reversal, SOI, mortality
- Findings:
- No difference in overall groups
- In patients with baseline thiamine deficiency (35% of total):
- Lower lactate
- Decreased mortality
 EGDT and AKI
EGDT and AKI

Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2/1/16
- Ancillary study to PROCESS Trial
- Evaluated impact of protocolized EGDT vs. standard care
- Finding: No difference in incidence/severity of AKI

 Out with the Old, In with the New
Out with the Old, In with the New
Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
Focusing on the changes from 2012
- Adopted Sepsis-3 definitions of sepsis and septic shock
- Sepsis: life-threatening organ dysfunction caused by a dysregulated host response to infection
- Septic shock: subset of sepsis with circulatory and cellular/metabolic dysfunction associated with a higher risk of mortality
- However, recognized that most of the studies forming the basis of guideline used traditional SIRS, sepsis, severe sepsis, septic shock
Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
- EGDT is gone as a specific recommendation
- Guide additional fluid by frequent reassessment of hemodynamic status
 If clinical examination dose not lead to clear diagnosis of volume status, use additional hemodynamic measures
If clinical examination dose not lead to clear diagnosis of volume status, use additional hemodynamic measures- Use dynamic rather than static variables to predict fluid responsiveness, where available
Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
-
- Optimize antimicrobial dosing based on accepted pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamics principles and particular drug properties in patients with sepsis/septic shock
- Increased incidence of renal and hepatic impairment
- Increased volume of distribution due to rapid expansion of ECV
- Initiate therapy with full, high-end loading dose to avoid frequent subtherapeutic levels
- Optimize antimicrobial dosing based on accepted pharmacokinetic/ pharmacodynamics principles and particular drug properties in patients with sepsis/septic shock

Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
-
- 7-10 days of antimicrobial therapy for most serious infections, but shorter duration for some (rapid clinical resolution after intra- abdominal source control, urinary sepsis, uncomplicated pyelonephritis)
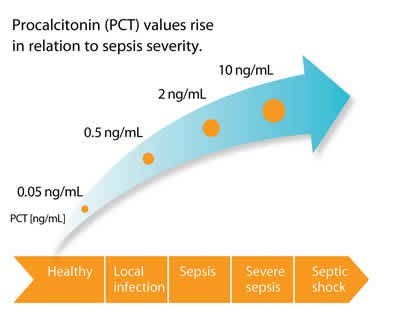
- Suggest use of procalcitonin to support shortening duration of antimicrobial therapy
Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
-
 Use prone positioning for ARDS with PaO2/FIO2 ratio < 150 (previously 100)
Use prone positioning for ARDS with PaO2/FIO2 ratio < 150 (previously 100)- No recommendation regarding use of Non-Invasive Ventilation (previously limited use based on risk/benefit assessment)
Surviving Sepsis Campaign 2016
Enteral feeding
-
- Use prokinetic agents for feeding intolerance
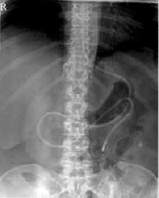 Place post-pyloric feeding tubes for feeding intolerance or if high risk for aspiration
Place post-pyloric feeding tubes for feeding intolerance or if high risk for aspiration
 A Beacon of Light
A Beacon of Light
![]()
The Marik Protocol
 Marik Protocol
Marik Protocol

Paul Marik, MBBCh
Chief of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine

Anti-thrombotic
Antiproliferative Antiagregant Anti•angiogenesis F°ru rLIGa W r W/V¥ MGa poprotein
Hem‹› t» iy Fibrinoli i metabolism
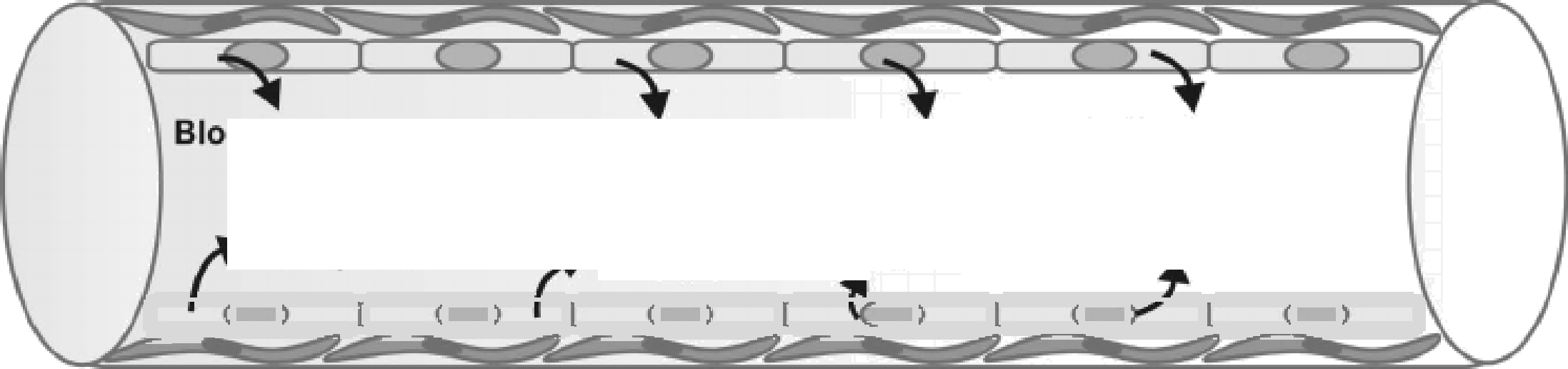
NORMAL EHDOTHELIUM
P’ Preies
Antip erative Prd§Urties
A t” nt Anti-a ogenesis
L”

![]()
![]()
![]()



DYSFUNCTIONAL ENDOTHELIUM



![]()

Basement
 membrane
membrane


Tight i• nction
Endothelial
nucleus
Intercellular
cleft
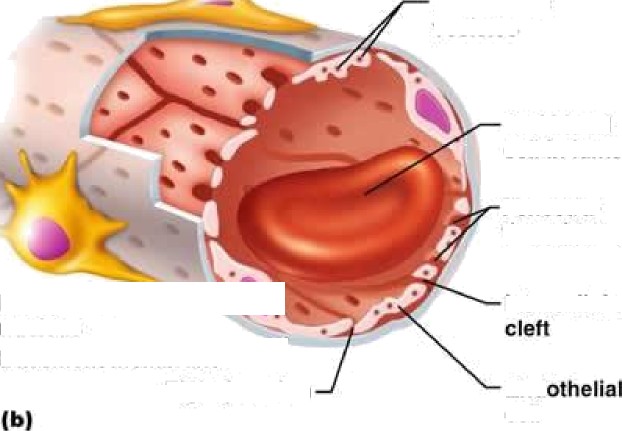
![]()
vesicles
Red blood
cell in lumen
Fenestra-
tions (pores)
Endothelial
nucleus
Basement membrane
“
Intercellular
Tight junction End
cell
Endothelial
![]()
Pinocytotic vesicles
(a)
Tight junction
Incomplete *“”
basement
(c) membrane
Pericyte Endothelial
Red blood
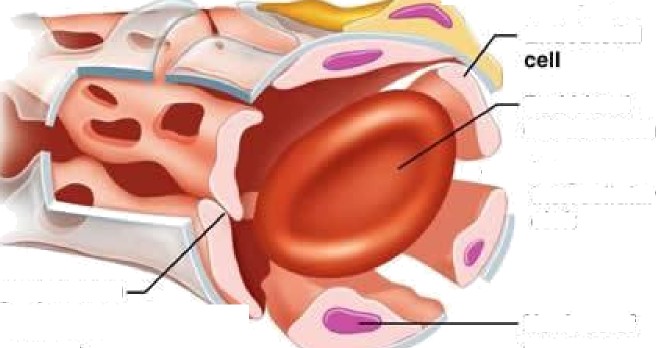
cell in lumen
Large interrellutar cleft
Nucleus of
endothelial cell
 Marik Protocol
Marik Protocol
-
- Vitamin C 1.5 g IV q6h
- Thiamine 200 mg IV q12h
- Hydrocortisone 50 mg IV q6h
- For 4 days, or until patient is discharged from the ICU
 Marik Protocol
Marik Protocol
-
- Entry criteria
- Severe sepsis or septic shock
- Procalcitonin ≥ 2 ng/ml
- Exclusions:
- < 18 years old
- Pregnant
- Limitations of care
- Retrospective before-after clinical study
- 7 months, 47 patients in each group
- Entry criteria
 Marik Protocol
Marik Protocol
-
- No differences between the two groups
- Study group mortality: 8.5%
- Control group mortality: 40.4%
- No deaths in the study group due to sepsis
- No patient in the study group developed progressive organ failure
- Mean time to vasopressor independence: 18 hours vs. 54 hours
 Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Vitamin C
-
- Potent antioxidant/free radical scavenger
- Restores other cellular antioxidants
- Essential co-factor for iron and copper-containing enzymes
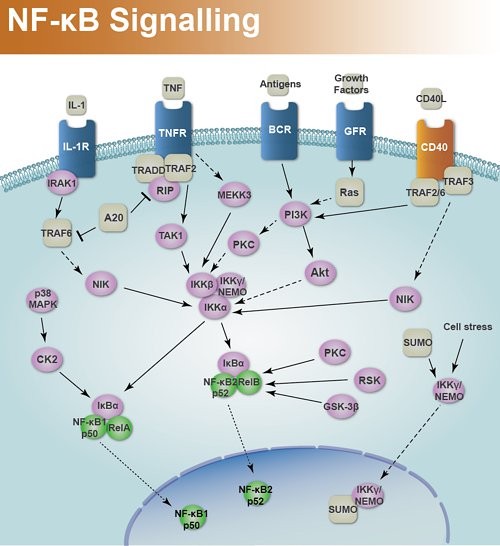
- Inhibits NF-κB activation

 Vitamin C and NF-κB
Vitamin C and NF-κB
 Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Vitamin C
-
- Potent antioxidant/free radical scavenger
- Restores other cellular antioxidants
- Essential co-factor for iron and copper-containing enzymes
- Inhibits NF-κB activation
- Increases endothelial and epithelial tight junctions
- Preserves endothelial function and microcirculatory flow
- Catecholamine synthesis and vasopressor sensitivity
 Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
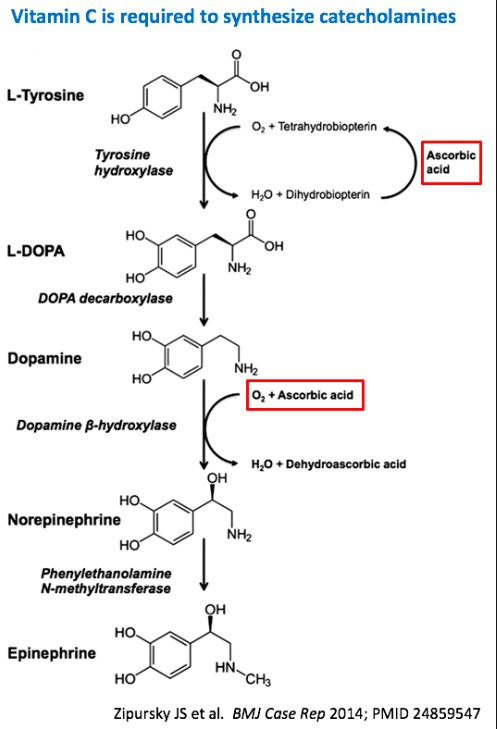 Vitamin C is required for catecholamine synthesis
Vitamin C is required for catecholamine synthesis
 Why add Hydrocortisone?
Why add Hydrocortisone?
- Vitamin C needs help getting into cells


![]()
6uany1yI
SVCT2
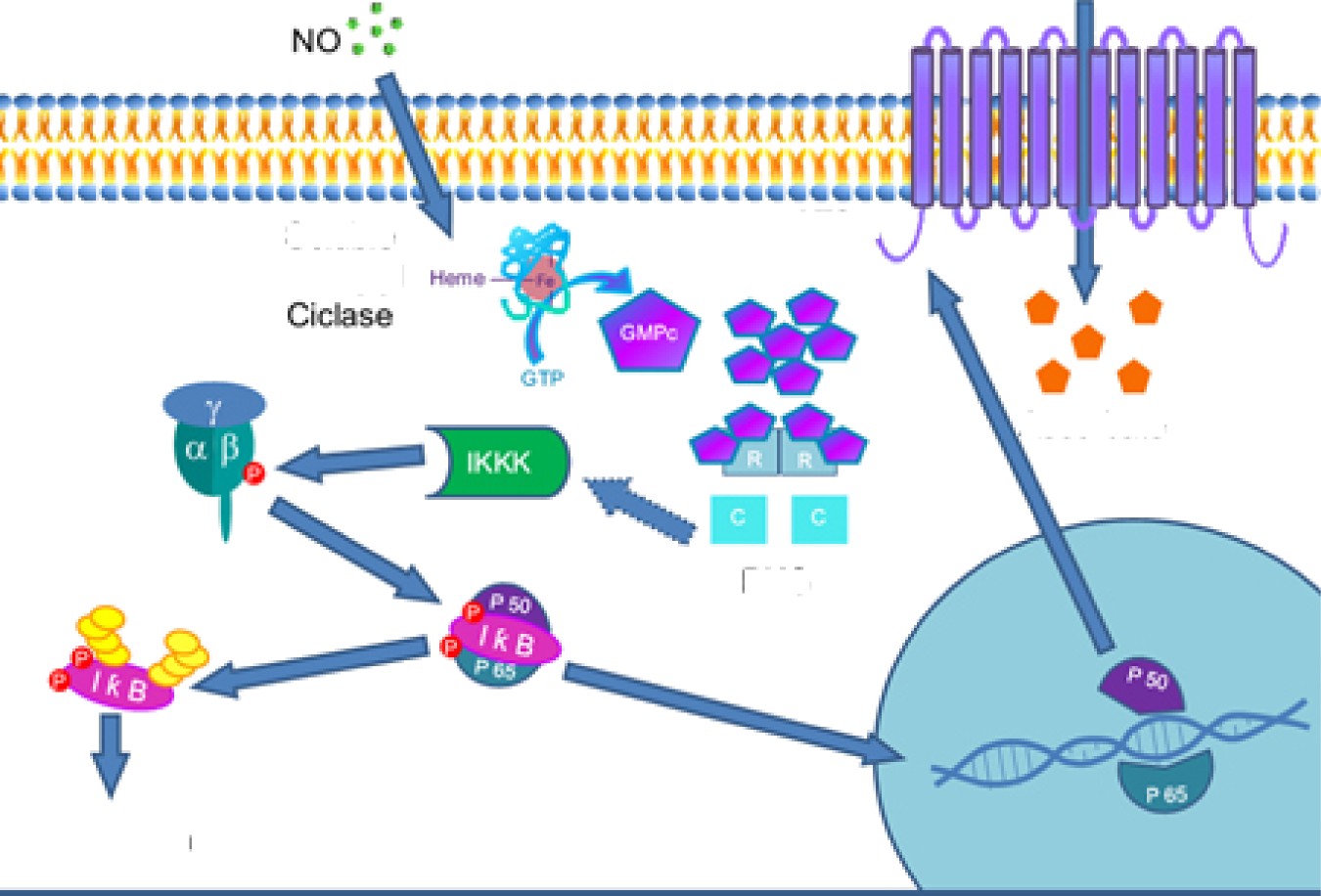
Ascorb«te
PKG
NfikB
 Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
- SVCT2
- Expression is down-regulated by pro- inflammatory cytokines
- Expression is up-regulated by corticosteroids
- Study of cultured endothelial cells + endotoxin
 Vitamin C alone: no help Steroids alone: no help
Vitamin C alone: no help Steroids alone: no help
Vitamin C + steroids: Restored function
 Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Marik Protocol: Mechanism?
Why do we need extra vitamin C?
- Levels are very low or undetectable in critical illness
- Intestinal receptor is saturable, so can’t restore levels with oral dosing
Why does thiamine help?
 Shunts metabolism of vitamin C away from oxalate (potential for renal crystallization)
Shunts metabolism of vitamin C away from oxalate (potential for renal crystallization)
 Marik Protocol: Application
Marik Protocol: Application
What are the ethics of implementing this protocol?
“Hardcore evidence-based medicine disciples may be aghast at using a therapy without a large multi-center RCT, whereas more integrative, theoretically-minded clinicians may be willing to consider it.”
— Josh Farkas, MD
 Bioethical Principles
Bioethical Principles
-
- Non-maleficence (“First, do no harm”)
- Harms of commission
 Harms of omission
Harms of omission
- Beneficence
- Autonomy
- Justice
- Non-maleficence (“First, do no harm”)
-
- Vitamin C: Oxaluria with potential for renal deposition and crystallization in patients with impaired renal function – but renal function improved more in the protocol group than in controls, and thiamine shunts vitamin C metabolism away from oxalate to CO2 production
- Thiamine: Rare reports of hypersensitivity or anaphylaxis, especially with repeated injections
Steroids in Severe Sepsis (HYPRESS Trial)
Steroids in Septic Shock:
CORTICUS Trial
(statistical significance not assessed)
- Hyperglycemia (≥ 150 mg/dl)
– ARI = 9.4%
– NNTH 10.6 (p=0.009)
– No statistically sig. difference in total insulin administered
- Secondary Infections
– ARI = 4.6%
– NNTH 21.7 (NS)
- Hyperglycemia (≥ 150 mg/dl)
– ARI = 13%
-
- NNTH 7.7
- Superinfection
- ARI = 5%
- NNTH 20
- New Septic Shock
- ARI = 4%
- NNTH 25
ARI = Absolute Risk Increase
-
- Annane – Effect of Treatment with Low Doses of Hydrocortisone and Fludrocortisone on Mortality in Septic Shock (JAMA 2002)
- Secondary Infection
- ARR 1% (NNTB 100)
- Vasopressor-associated harm
- ARI 2% (NNTH 50)
- Hyperglycemia – not reported
- Secondary Infection
- NB: All 3 studies, plus VANISH Trial, showed no mortality increase with steroids
- Annane – Effect of Treatment with Low Doses of Hydrocortisone and Fludrocortisone on Mortality in Septic Shock (JAMA 2002)
 Costs
Costs
-
- IV Vitamin C: $88 – 260 for 4-day course (drug only)
- IV Thiamine: $45 for 4-day course (drug only)
- Hydrocortisone: ~ $80 (drug only)
 Implementation Options: A Proposal
Implementation Options: A Proposal
Patients with Refractory Septic Shock
Severe Sepsis and Non- Refractory Septic Shock
- Already receiving steroids
- No/minimal predicted harm from adding Vitamin C and thiamine
- Reasonable to endorse use in this group
- These patients would not otherwise receive steroids per SSC Guidelines
- Inadequate Evidence- Based literature to justify endorsement
- Therefore, leave to individual practitioners to choose
 Some bad news…
Some bad news…
- IV Vitamin C has a single producer:


Still…

 Sepsis Update 2017
Sepsis Update 2017
Jim Leo, MD [email protected]










Để lại một bình luận